Page 34 - Guide Book
P. 34
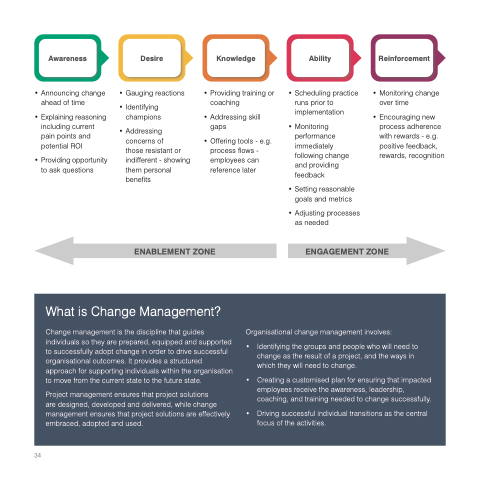
Awareness
• Announcing change ahead of time
• Explaining reasoning including current pain points and potential ROI
• Providing opportunity to ask questions
• Gauging reactions
• Identifying champions
• Addressing concerns of
those resistant or indifferent - showing them personal benefits
• • •
Providing training or coaching
Addressing skill gaps
Offering tools - e.g. process flows - employees can reference later
• Scheduling practice runs prior to implementation
• Monitoring performance immediately following change and providing feedback
• Setting reasonable goals and metrics
• Adjusting processes as needed
• Monitoring change over time
• Encouraging new process adherence with rewards - e.g. positive feedback, rewards, recognition
Desire
Knowledge
Ability
Reinforcement
ENABLEMENT ZONE
ENGAGEMENT ZONE
What is Change Management?
Change management is the discipline that guides individuals so they are prepared, equipped and supported to successfully adopt change in order to drive successful organisational outcomes. It provides a structured approach for supporting individuals within the organisation to move from the current state to the future state.
Project management ensures that project solutions
are designed, developed and delivered, while change management ensures that project solutions are effectively embraced, adopted and used.
Organisational change management involves:
• Identifying the groups and people who will need to change as the result of a project, and the ways in which they will need to change.
• Creating a customised plan for ensuring that impacted employees receive the awareness, leadership, coaching, and training needed to change successfully.
• Driving successful individual transitions as the central focus of the activities.
34