Page 81 - Community pharmcy practice E-book 2025
P. 81
02/11/2025, 00:10 Otic & Ophthalmic Disorders | Dermatological Disorders
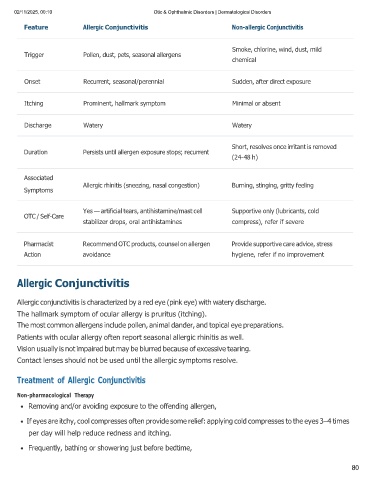
Feature Allergic Conjunctivitis Non-allergic Conjunctivitis
Trigger Pollen, dust, pets, seasonal allergens Smoke, chlorine, wind, dust, mild
chemical
Onset
Itching Recurrent, seasonal/perennial Sudden, after direct exposure
Discharge
Prominent, hallmark symptom Minimal or absent
Duration
Watery Watery
Associated
Symptoms Persists until allergen exposure stops; recurrent Short, resolves once irritant is removed
(24-48 h)
OTC / Self-Care
Allergic rhinitis (sneezing, nasal congestion) Burning, stinging, gritty feeling
Pharmacist
Action Yes — artificial tears, antihistamine/mast cell Supportive only (lubricants, cold
stabilizer drops, oral antihistamines compress), refer if severe
Recommend OTC products, counsel on allergen Provide supportive care advice, stress
avoidance hygiene, refer if no improvement
Allergic Conjunctivitis
Allergic conjunctivitis is characterized by a red eye (pink eye) with watery discharge.
The hallmark symptom of ocular allergy is pruritus (itching).
The most common allergens include pollen, animal dander, and topical eye preparations.
Patients with ocular allergy often report seasonal allergic rhinitis as well.
Vision usually is not impaired but may be blurred because of excessive tearing.
Contact lenses should not be used until the allergic symptoms resolve.
Treatment of Allergic Conjunctivitis
Non-pharmacological Therapy
Removing and/or avoiding exposure to the offending allergen,
If eyes are itchy, cool compresses often provide some relief: applying cold compresses to the eyes 3–4 times
per day will help reduce redness and itching.
Frequently, bathing or showering just before bedtime,
80