Page 103 - A Handbook for Academia, Industry and Policymakers: Reinforcing the Innovation-Employability Nexus in the Mediterranean
P. 103
102 REINFORCING THE INNOVATION-EMPLOYABILITY NEXUS IN THE MEDITERRANEAN REINFORCING THE INNOVATION-EMPLOYABILITY NEXUS IN THE MEDITERRANEAN 103
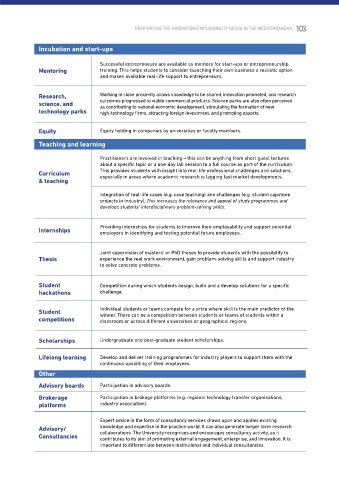
Tools and resources Incubation and start-ups
Knowledge exchange between academia and industry comes in many different shapes and sizes. Successful entrepreneurs are available as mentors for start-ups or entrepreneurship
Collaborative innovation certainly is a key area, but there are many more opportunities to collaborate Mentoring training. This helps students to consider launching their own business a realistic option
and create partnerships – intersectoral mobility, curriculum development, teaching and learning are and makes available real-life support to entrepreneurs.
some pertinent examples.
Research, Working in close proximity allows knowledge to be shared, innovation promoted, and research
Potential contributions to the innovation ecosystem by academia, industry, and policymakers outcomes progressed to viable commercial products. Science parks are also often perceived
Table 4 science, and as contributing to national economic development, stimulating the formation of new
technology parks high-technology firms, attracting foreign investment, and promoting exports.
Instrument Format/Function
Research Equity Equity holding in companies by universities or faculty members.
Support industry in solving concrete problems and innovation challenges. This provides Teaching and learning
Contract flexible funds that can be used freely for other research, infrastructural or maintenance
research purposes. There is also the possibility of aligning the academic research strategy with Practitioners are involved in teaching – this can be anything from short guest lectures
industrially relevant themes and expand the network.
about a specific topic or a one-day lab session to a full course as part of the curriculum.
Curriculum This provides students with insight into real-life professional challenges and solutions,
Joint research projects allow for a number of benefits on both sides. They provide & teaching especially in areas where academic research is lagging fast market developments.
industry with the latest, specialised, in-depth research know-how in academia, while
Joint research academia develops awareness of latest trends in industry. This is also a chance for Integration of real-life cases (e.g. case teaching) and challenges (e.g. student capstone
academic research to be inspired by application-derived questions. Other benefits are
projects the development of an extended network, the benefits of out-of-the-box thinking, projects in industry). This increases the relevance and appeal of study programmes and
increased mutual understanding of each other’s perspectives, interests, and challenges, develops students’ interdisciplinary problem-solving skills.
and last but not least, the screening of new talent for employment.
Providing internships for students to improve their employability and support potential
Internships
Co-created Funding of joint Institutes or Labs (infrastructure and PhD students) or co-created employers in identifying and testing potential future employees.
research research centres enhance the long-term innovative capacity of both the corporate and
academic partners, allow for state-of-the-art infrastructure and strengthening of the
centres or joint organisation’s competitiveness, while alleviating public budget pressures. These Joint supervision of masters’ or PhD theses to provide students with the possibility to
Institutes/Labs initiatives can go as far as whole research, science and technology parks. Thesis experience the real work environment, gain problem-solving skills and support industry
to solve concrete problems.
Cross- Part-time positions for industry researchers at the university and vice-versa (e.g.
appointments cross-appointments) which develops mutual knowledge of needs and challenges, and Student Competition during which students design, build and a develop solutions for a specific
understanding of each other’s methods, concepts, and attitudes. hackathons challenge.
Patent and Student Individual students or teams compete for a prize where skill is the main predictor of the
licensing Commercialising research results through patenting and licensing these outputs. competitions winner. There can be a competition between students or teams of students within a
classroom or across different universities or geographical regions.
agreements
Scholarships Undergraduate and post-graduate student scholarships.
Industry
research The aim is to develop and support industry-academia research partnerships. Lifelong learning Develop and deliver training programmes for industry players to support them with the
fellowships continuous upskilling of their employees.
Other
Research grants, gifts, endowments, donations (financial or equipment), general or
Grants directed to specific departments or academics. Advisory boards Participation in advisory boards.
Brokerage Participation in brokage platforms (e.g. regional technology transfer organisations,
platforms industry association).
Endowed/ Sponsoring chairs (internationally competitive salary, possibly also including start-up
Sponsored funds, research infrastructures) supports academia in hiring a high-level researcher to Expert advice in the form of consultancy services draws upon and applies existing
strengthen a specific research area. At the same time, the access to the researcher can
chairs strengthen a company’s key competences. Advisory/ knowledge and expertise in the practice world. It can also generate longer term research
Consultancies collaborations. The University recognises and encourages consultancy activity, as it
contributes to its aim of promoting external engagement, enterprise, and innovation. It is
important to differentiate between institutional and individual consultancies.