Page 105 - A Handbook for Academia, Industry and Policymakers: Reinforcing the Innovation-Employability Nexus in the Mediterranean
P. 105
104 REINFORCING THE INNOVATION-EMPLOYABILITY NEXUS IN THE MEDITERRANEAN REINFORCING THE INNOVATION-EMPLOYABILITY NEXUS IN THE MEDITERRANEAN 105
Linking demand to supply in employability
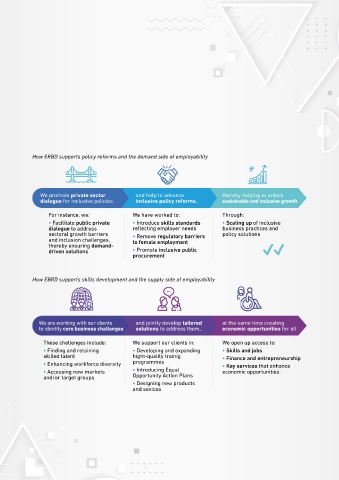
EBRD European Bank for Reconstruction and How ERBD supports policy reforms and the demand side of employability
Development Employment & Skills Programmes
The EBRD has developed a unique private sector focused • At an operational level, EBRD defines economic We promote private sector and help to advance thereby helping to unlock
approach to economic inclusion which integrates a focus opportunities as access to jobs and skills, finance and dialogue for inclusive policies inclusive policy reforms, sustainable and inclusive growth
on gender into the Bank’s transition mandate to support entrepreneurship and services.
countries through projects and policy engagement in • Annual inclusion ‘gap’ assessments measure the extent
their transition towards sustainable and inclusive market to which women, young people or people in remote For instance, we: We have worked to: Through:
economies. The EBRD promotes inclusive market economies regions face disproportionate challenges in accessing • Facilitate public private • Introduce skills standards • Scaling up of inclusive
by harnessing the power of the private sector to create employment, entrepreneurship or services. These ‘gaps’ dialogue to address reflecting employer needs business practices and
equitable access to economic opportunity for all. This distinct allow for the Bank to prioritise investments to address sectoral growth barriers • Remove regulatory barriers policy solutions
approach to economic inclusion makes use of the Bank’s key inclusion challenges through its investment and policy and inclusion challenges, to female employment
private sector engagement to support its clients in addressing activities across the region. thereby ensuring demand- • Promote inclusive public
key operational challenges – whilst at the same time opening driven solutions procurement
economic opportunities to underserved groups. On the policy side, the EBRD contributes to policy framing,
negotiations, and decision-making. Inclusive investments
The Bank works pro-actively with clients across sectors such provide the basis for policy engagement where the EBRD
as manufacturing, retail and tourism, agribusiness, power and brings together private sector employers (its clients and other How EBRD supports skills development and the supply side of employability
energy, natural resources and financial institutions to achieve interested companies) and education authorities in order to
measurable and verifiable inclusion outcomes. Economic raise vocational skills standards based on the requirements of
inclusion is fully integrated into the EBRD’s transition mandate employers and to enhance the effectiveness of dual education
and its project selection, appraisal and evaluation processes models (such as apprenticeships). Until today, the EBRD has
across all sectors and regions. invested EUR 11.4 billion in more than 290 projects with
private sector companies targeted at gender and economic
The EBRD’s inclusion approach is based on a clear definition inclusion. We are working with our clients and jointly develop tailored at the same time creating
and robust analytical framework: to identity core business challenges solutions to address them, economic opportunities for all
www.ebrd.com
• Based on the concept of equality of opportunity, the EBRD These chellenges include: We support our clients in: We open up access to:
defines economic inclusion as the opening up of economic
opportunities to previously under-served social groups, • Finding and retaining • Developing and expanding • Skills and jobs
regardless of circumstances beyond their control, such as skilled talent hight-quality trainig • Finance and entrepreneurship
their gender, place of birth, socio-economic environment • Enhancing workforce diversity programmes • Key services that enhance
or age. • Accessing new markets • Introducing Equal economic opportunities.
and/or target groups Opportunity Action Plans
• Designing new products
and sevices