Page 71 - BFSI CHRONICLE 10 th Issue (2nd Annual Issue ) .indd
P. 71
BFSI Chronicle, 2 Annual Issue, 10 Edition July 2022
nd
th
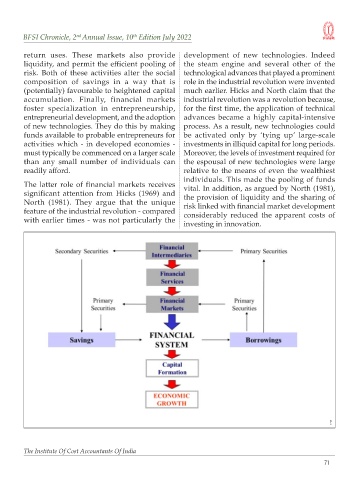
return uses. These markets also provide development of new technologies. Indeed
liquidity, and permit the efficient pooling of the steam engine and several other of the
risk. Both of these activities alter the social technological advances that played a prominent
composition of savings in a way that is role in the industrial revolution were invented
(potentially) favourable to heightened capital much earlier. Hicks and North claim that the
accumulation. Finally, financial markets industrial revolution was a revolution because,
foster specialization in entrepreneurship, for the first time, the application of technical
entrepreneurial development, and the adoption advances became a highly capital-intensive
of new technologies. They do this by making process. As a result, new technologies could
funds available to probable entrepreneurs for be activated only by ‘tying up’ large-scale
activities which - in developed economies - investments in illiquid capital for long periods.
must typically be commenced on a larger scale Moreover, the levels of investment required for
than any small number of individuals can the espousal of new technologies were large
readily afford. relative to the means of even the wealthiest
individuals. This made the pooling of funds
The latter role of financial markets receives
vital. In addition, as argued by North (1981),
significant attention from Hicks (1969) and the provision of liquidity and the sharing of
North (1981). They argue that the unique risk linked with financial market development
feature of the industrial revolution - compared considerably reduced the apparent costs of
with earlier times - was not particularly the
investing in innovation.
!
The Institute Of Cost Accountants Of India
71