Page 5 - 53-Peptic ulcer diseases (Loét dạ dày)
P. 5
CHAPTER 53 Peptic Ulcer Disease 809
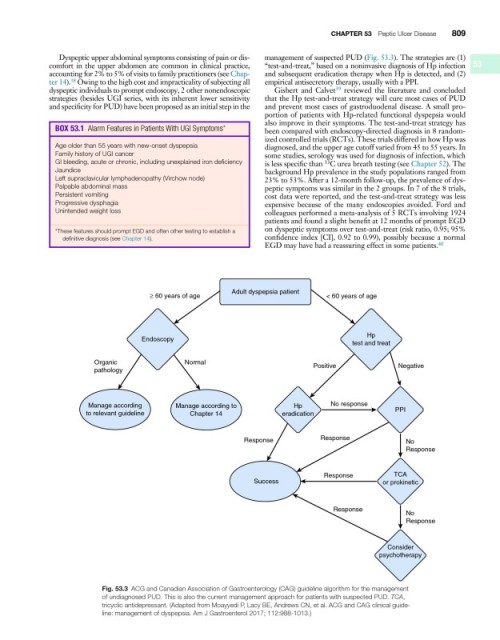
Dyspeptic upper abdominal symptoms consisting of pain or dis- management of suspected PUD (Fig. 53.3). The strategies are (1)
comfort in the upper abdomen are common in clinical practice, “test-and-treat,” based on a noninvasive diagnosis of Hp infection 53
accounting for 2% to 5% of visits to family practitioners (see Chap- and subsequent eradication therapy when Hp is detected, and (2)
ter 14). Owing to the high cost and impracticality of subjecting all empirical antisecretory therapy, usually with a PPI.
38
dyspeptic individuals to prompt endoscopy, 2 other nonendoscopic Gisbert and Calvet reviewed the literature and concluded
39
strategies (besides UGI series, with its inherent lower sensitivity that the Hp test-and-treat strategy will cure most cases of PUD
and specificity for PUD) have been proposed as an initial step in the and prevent most cases of gastroduodenal disease. A small pro-
portion of patients with Hp-related functional dyspepsia would
also improve in their symptoms. The test-and-treat strategy has
BOX 53�1 Alarm Features in Patients With UGI Symptoms* been compared with endoscopy-directed diagnosis in 8 random-
ized controlled trials (RCTs). These trials differed in how Hp was
Age older than 55 years with new-onset dyspepsia diagnosed, and the upper age cutoff varied from 45 to 55 years. In
Family history of UGI cancer some studies, serology was used for diagnosis of infection, which
GI bleeding, acute or chronic, including unexplained iron deficiency is less specific than C urea breath testing (see Chapter 52). The
13
Jaundice background Hp prevalence in the study populations ranged from
Left supraclavicular lymphadenopathy (Virchow node) 23% to 53%. After a 12-month follow-up, the prevalence of dys-
Palpable abdominal mass peptic symptoms was similar in the 2 groups. In 7 of the 8 trials,
Persistent vomiting cost data were reported, and the test-and-treat strategy was less
Progressive dysphagia expensive because of the many endoscopies avoided. Ford and
Unintended weight loss colleagues performed a meta-analysis of 5 RCTs involving 1924
patients and found a slight benefit at 12 months of prompt EGD
*These features should prompt EGD and often other testing to establish a on dyspeptic symptoms over test-and-treat (risk ratio, 0.95; 95%
definitive diagnosis (see Chapter 14). confidence index [CI], 0.92 to 0.99), possibly because a normal
EGD may have had a reassuring effect in some patients. 40
Adult dyspepsia patient
≥ 60 years of age < 60 years of age
Hp
Endoscopy
test and treat
Organic Normal Positive Negative
pathology
Manage according Manage according to Hp No response
to relevant guideline Chapter 14 eradication PPI
Response Response No
Response
Response TCA
Success or prokinetic
Response
No
Response
Consider
psychotherapy
Fig. 53.3 ACG and Canadian Association of Gastroenterology (CAG) guideline algorithm for the management
of undiagnosed PUD. This is also the current management approach for patients with suspected PUD. TCA,
tricyclic antidepressant. (Adapted from Moayyedi P, Lacy BE, Andrews CN, et al. ACG and CAG clinical guide-
line: management of dyspepsia. Am J Gastroenterol 2017; 112:988-1013.)