Page 16 - Gastrointestinal Bleeding (Xuất huyết tiêu hóa)
P. 16
290 PART III Symptoms, Signs, and Biopsychosocial Issues
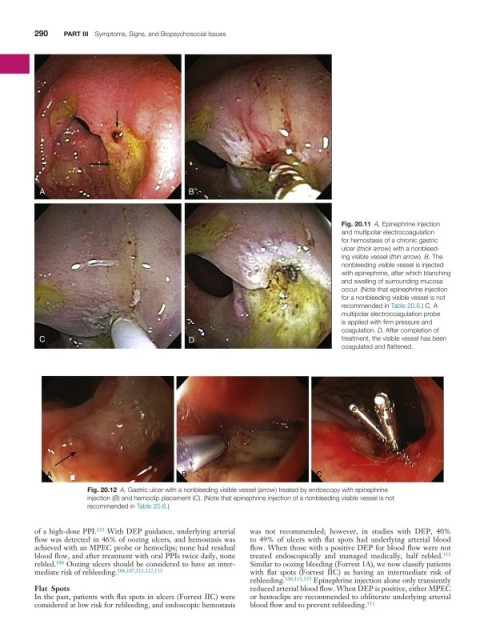
A B
Fig. 20.11 A, Epinephrine injection
and multipolar electrocoagulation
for hemostasis of a chronic gastric
ulcer (thick arrow) with a nonbleed-
ing visible vessel (thin arrow). B, The
nonbleeding visible vessel is injected
with epinephrine, after which blanching
and swelling of surrounding mucosa
occur. (Note that epinephrine injection
for a nonbleeding visible vessel is not
recommended in Table 20.6.) C, A
multipolar electrocoagulation probe
is applied with firm pressure and
coagulation. D, After completion of
C D treatment, the visible vessel has been
coagulated and flattened.
A B C
Fig. 20.12 A, Gastric ulcer with a nonbleeding visible vessel (arrow) treated by endoscopy with epinephrine
injection (B) and hemoclip placement (C). (Note that epinephrine injection of a nonbleeding visible vessel is not
recommended in Table 20.6.)
of a high-dose PPI. 135 With DEP guidance, underlying arterial was not recommended; however, in studies with DEP, 40%
flow was detected in 46% of oozing ulcers, and hemostasis was to 49% of ulcers with flat spots had underlying arterial blood
achieved with an MPEC probe or hemoclips; none had residual flow. When those with a positive DEP for blood flow were not
blood flow, and after treatment with oral PPIs twice daily, none treated endoscopically and managed medically, half rebled. 111
rebled. 106 Oozing ulcers should be considered to have an inter- Similar to oozing bleeding (Forrest 1A), we now classify patients
mediate risk of rebleeding. 106,107,111,112,135 with flat spots (Forrest IIC) as having an intermediate risk of
rebleeding. 106,111,135 Epinephrine injection alone only transiently
Flat Spots reduced arterial blood flow. When DEP is positive, either MPEC
In the past, patients with flat spots in ulcers (Forrest IIC) were or hemoclips are recommended to obliterate underlying arterial
considered at low risk for rebleeding, and endoscopic hemostasis blood flow and to prevent rebleeding. 111