Page 139 - FULL REPORT 30012024
P. 139
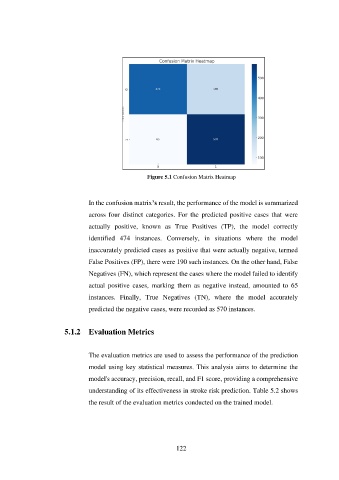
Figure 5.1 Confusion Matrix Heatmap
In the confusion matrix’s result, the performance of the model is summarized
across four distinct categories. For the predicted positive cases that were
actually positive, known as True Positives (TP), the model correctly
identified 474 instances. Conversely, in situations where the model
inaccurately predicted cases as positive that were actually negative, termed
False Positives (FP), there were 190 such instances. On the other hand, False
Negatives (FN), which represent the cases where the model failed to identify
actual positive cases, marking them as negative instead, amounted to 65
instances. Finally, True Negatives (TN), where the model accurately
predicted the negative cases, were recorded as 570 instances.
5.1.2 Evaluation Metrics
The evaluation metrics are used to assess the performance of the prediction
model using key statistical measures. This analysis aims to determine the
model's accuracy, precision, recall, and F1 score, providing a comprehensive
understanding of its effectiveness in stroke risk prediction. Table 5.2 shows
the result of the evaluation metrics conducted on the trained model.
122