Page 37 - Microsoft Word - 20120528 Unesco study
P. 37
3.5 Damage mechanisms
A road might be damaged in many different ways and may display different signs of damage;
Factors to observe are:
- Seriousness of the damage.
- Scope of the damage.
- Type of road.
In this study the focus is on damage as result of flooding. There is an overlap with the
structural damages due to the accepted wear and tear of the lifetime of the road. The age of
the road will therefore have a major influence. Damaged or weakened parts of a road will
easily be worsened by flooding.
For possible damages a distinction is made for that caused directly or indirectly by floods.
- Directly
Direct damage of a road is readily noticed. In most cases this will be caused by erosion
of floating water. Therefore the road may be completely washed away. Roads which
are built on dikes or embankments will have other possible failure mechanisms, which
are also show signs of direct damage.
- Indirectly
When a road construction remains under water for a while, the water will penetrate
into the pavement construction. Saturated unbound materials have a disadvantage in
that they lose their strength. When the unbound materials in a road construction are
saturated and the road is trafficked the bound materials will be over loaded and the
lifetime of the construction will be reduced significantly. However this failure is mainly
caused by flooding, and this failure will not always be related to the flood. These
failures will therefore not be included in the calculations.
Using the flooding data the total amount of roads, which were actually flooded, can be
determined. Not all of these roads are expected to be damaged. To get an accurate impression
of the actual damaged roads the ratio between flooded roads and actual damaged roads is
determined. Since this data is not available yet for the state Tabasco, assumptions are made
based on expert judgment.
It is known that a significant amount of the flooded roads are so damaged that a total
reconstruction of the road is required. Smaller damages on the roads are not always directly
noticed and these disadvantages are encountered only after some time. So this study is
focused on roads totally destroyed by floods. Heavier constructions are expected to be less
sensitive flood damage in comparison with lighter constructions. So a distinction is made for
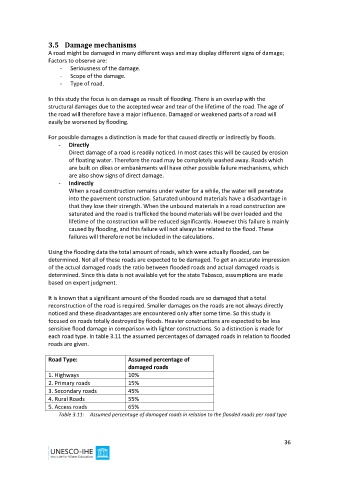
each road type. In table 3.11 the assumed percentages of damaged roads in relation to flooded
roads are given.
Road Type: Assumed percentage of
damaged roads
1. Highways 10%
2. Primary roads 15%
3. Secondary roads 45%
4. Rural Roads 55%
5. Access roads 65%
Table 3.11: Assumed percentage of damaged roads in relation to the flooded roads per road type
36