Page 13 - MF3010Series Service Manual (Rev.0) (1)-017-045 (1)
P. 13
2 Technical Overview > Image Formation System > Overview/Configuration > Development Block
2-14
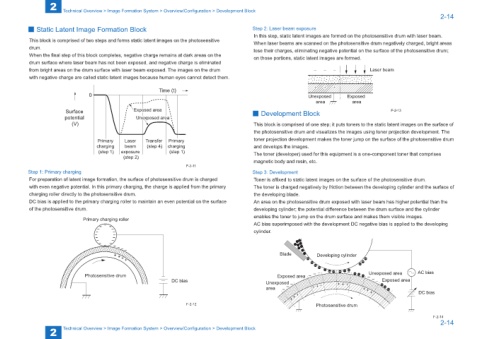
■ Static Latent Image Formation Block Step 2: Laser beam exposure
In this step, static latent images are formed on the photosensitive drum with laser beam.
This block is comprised of two steps and forms static latent images on the photosensitive When laser beams are scanned on the photosensitive drum negatively charged, bright areas
drum. lose their charges, eliminating negative potential on the surface of the photosensitive drum;
When the final step of this block completes, negative charge remains at dark areas on the on those portions, static latent images are formed.
drum surface where laser beam has not been exposed, and negative charge is eliminated
from bright areas on the drum surface with laser beam exposed. The images on the drum Laser beam
with negative charge are called static latent images because human eyes cannot detect them.
Time (t)
0 Unexposed Exposed
area area
Surface Exposed area ■ Development Block F-2-13
potential Unexposed area
(V) This block is comprised of one step; it puts toners to the static latent images on the surface of
the photosensitive drum and visualizes the images using toner projection development. The
Primary Laser Transfer Primary toner projection development makes the toner jump on the surface of the photosensitive drum
charging beam (step 4) charging and develops the images.
(step 1) exposure (step 1) The toner (developer) used for this equipment is a one-component toner that comprises
(step 2)
magnetic body and resin, etc.
F-2-11
Step 1: Primary charging Step 3: Development
For preparation of latent image formation, the surface of photosensitive drum is charged Toner is affixed to static latent images on the surface of the photosensitive drum.
with even negative potential. In this primary charging, the charge is applied from the primary The toner is charged negatively by friction between the developing cylinder and the surface of
charging roller directly to the photosensitive drum. the developing blade.
DC bias is applied to the primary charging roller to maintain an even potential on the surface An area on the photosensitive drum exposed with laser beam has higher potential than the
of the photosensitive drum. developing cylinder; the potential difference between the drum surface and the cylinder
enables the toner to jump on the drum surface and makes them visible images.
Primary charging roller
AC bias superimposed with the development DC negative bias is applied to the developing
cylinder.
Blade Developing cylinder
Photosensitive drum Exposed area Unexposed area AC bias
DC bias Unexposed Exposed area
area
DC bias
F-2-12 Photosensitive drum
F-2-14
2-14
2 Technical Overview > Image Formation System > Overview/Configuration > Development Block