Page 15 - MF3010Series Service Manual (Rev.0) (1)-017-045 (1)
P. 15
2 Technical Overview > Image Formation System > High-Voltage Control > Generating Transfer Bias
2-16
High-Voltage Control ■ Generating Developing Bias
■ Overview The developing bias is a DC negative bias that is output to affix toner to the static latent
images formed on the photosensitive drum. This bias is a development DC and AC
This circuit is comprised of the circuits that apply biases to the primary charging roller, superimposed bias and generated by the development high-voltage generating circuit in the
developing cylinder, transfer roller, and the fixing control circuit. The CPU of the engine high-voltage power supply circuit.
controller controls the high-voltage power supply circuit to generate these biases. The fixing The high-voltage power supply circuit applies the generated developing bias to the developing
control circuit executes heater control of the fixing assembly according to the instruction by cylinder at a specified timing.
the CPU of the engine controller. The developing bias varies in conjunction with the primary charging bias according to the
The following is the block diagram of this circuit. information of image density sent from the main controller.
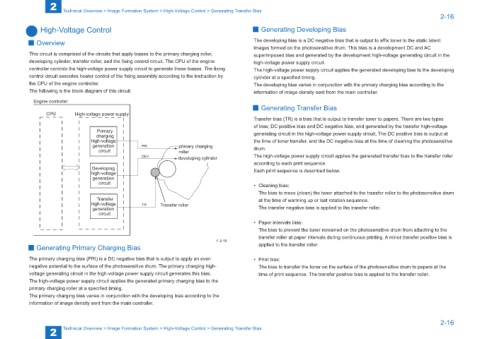
Engine controller
■ Generating Transfer Bias
CPU High-voltage power supply
Transfer bias (TR) is a bias that is output to transfer toner to papers. There are two types
of bias; DC positive bias and DC negative bias, and generated by the transfer high-voltage
Primary
charging generating circuit in the high-voltage power supply circuit. The DC positive bias is output at
high-voltage the time of toner transfer, and the DC negative bias at the time of cleaning the photosensitive
generation PRI primary charging drum.
circuit roller
DEV developing cylinder The high-voltage power supply circuit applies the generated transfer bias to the transfer roller
according to each print sequence.
Developing Each print sequence is described below.
high-voltage
generation
circuit
• Cleaning bias:
The bias to move (clean) the toner attached to the transfer roller to the photosensitive drum
Transfer at the time of warming up or last rotation sequence.
high-voltage TR Transfer roller
generation The transfer negative bias is applied to the transfer roller.
circuit
• Paper intervals bias:
The bias to prevent the toner remained on the photosensitive drum from attaching to the
transfer roller at paper intervals during continuous printing. A minor transfer positive bias is
F-2-19
■ Generating Primary Charging Bias applied to the transfer roller.
The primary charging bias (PRI) is a DC negative bias that is output to apply an even • Print bias:
negative potential to the surface of the photosensitive drum. The primary charging high- The bias to transfer the toner on the surface of the photosensitive drum to papers at the
voltage generating circuit in the high-voltage power supply circuit generates this bias. time of print sequence. The transfer positive bias is applied to the transfer roller.
The high-voltage power supply circuit applies the generated primary charging bias to the
primary charging roller at a specified timing.
The primary charging bias varies in conjunction with the developing bias according to the
information of image density sent from the main controller.
2-16
2 Technical Overview > Image Formation System > High-Voltage Control > Generating Transfer Bias