Page 45 - RCM - A practical Guide_V1
P. 45
RCM - A Practical Guide
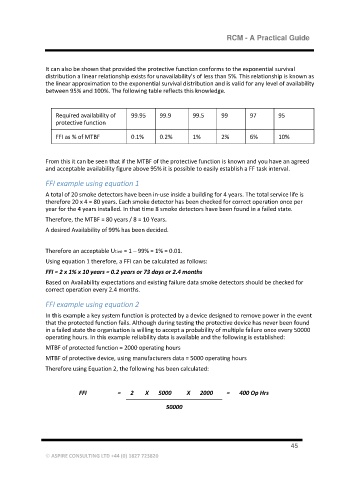
It can also be shown that provided the protective function conforms to the exponential survival
distribution a linear relationship exists for unavailability’s of less than 5%. This relationship is known as
the linear approximation to the exponential survival distribution and is valid for any level of availability
between 95% and 100%. The following table reflects this knowledge.
Required availability of 99.95 99.9 99.5 99 97 95
protective function
FFI as % of MTBF 0.1% 0.2% 1% 2% 6% 10%
From this it can be seen that if the MTBF of the protective function is known and you have an agreed
and acceptable availability figure above 95% it is possible to easily establish a FF task interval.
FFI example using equation 1
A total of 20 smoke detectors have been in-use inside a building for 4 years. The total service life is
therefore 20 x 4 = 80 years. Each smoke detector has been checked for correct operation once per
year for the 4 years installed. In that time 8 smoke detectors have been found in a failed state.
Therefore, the MTBF = 80 years / 8 = 10 Years.
A desired Availability of 99% has been decided.
Therefore an acceptable Utive = 1 – 99% = 1% = 0.01.
Using equation 1 therefore, a FFI can be calculated as follows:
FFI = 2 x 1% x 10 years = 0.2 years or 73 days or 2.4 months
Based on Availability expectations and existing failure data smoke detectors should be checked for
correct operation every 2.4 months.
FFI example using equation 2
In this example a key system function is protected by a device designed to remove power in the event
that the protected function fails. Although during testing the protective device has never been found
in a failed state the organisation is willing to accept a probability of multiple failure once every 50000
operating hours. In this example reliability data is available and the following is established:
MTBF of protected function = 2000 operating hours
MTBF of protective device, using manufacturers data = 5000 operating hours
Therefore using Equation 2, the following has been calculated:
FFI = 2 X 5000 X 2000 = 400 Op Hrs
50000
45
© ASPIRE CONSULTING LTD +44 (0) 1827 723820