Page 32 - Theoretical and Practical Interpretation of Investment Attractiveness
P. 32
Taking this into account, the investment climate should be stable in the long term, and
the investment climate should be variable depending on the demand for (consumed) factors
(resources) involved in the stages of social reproduction.
In modern socio-economic conditions, investment penetration depends on the
development of innovative industries and the development of innovative entrepreneurship,
the investment climate and the investment mechanism.
In the course of studying scientific research conducted on the regional economy, in this
study, factors indicating the investment attractiveness of regions were grouped into a single
system. It summarizes and classifies points of view and scientific and practical views as main
groups, reflecting the complex indicators of the region (Table 1.2.3).
Research shows that with a good investment climate, on the one hand, it is possible to
increase domestic investment and increase savings in relation to consumption in the structure
of planned expenses. This is a guarantee of high rates of economic growth.
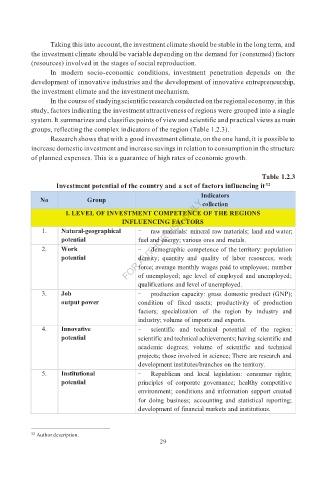
Table 1.2.3
Investment potential of the country and a set of factors influencing it
32
Indicators
No Group
collection
I. LEVEL OF INVESTMENT COMPETENCE OF THE REGIONS
INFLUENCING FACTORS
1. Natural-geographical raw materials: mineral raw materials; land and water;
potential fuel and energy; various ores and metals.
2. Work demographic competence of the territory: population
potential density; quantity and quality of labor resources; work
force; average monthly wages paid to employees; number
of unemployed; age level of employed and unemployed;
qualifications and level of unemployed.
3. Job production capacity: gross domestic product (GNP);
output power condition of fixed assets; productivity of production
factors; specialization of the region by industry and
industry; volume of imports and exports.
4. Innovative scientific and technical potential of the region:
potential scientific and technical achievements; having scientific and
academic degrees; volume of scientific and technical
projects; those involved in science; There are research and
development institutes/branches on the territory.
5. Institutional Republican and local legislation: consumer rights;
potential principles of corporate governance; healthy competitive
environment; conditions and information support created
for doing business; accounting and statistical reporting;
development of financial markets and institutions.
32
Author description.
29