Page 100 - Pharmaceutical_Analytical_Chemistry_1_Theoretical_Notes_Level_1
P. 100
Mansoura National University
Pharm D-Clinical Pharmacy Program Level 1 Pharm. Anal. Chem. 1 (PC 101)
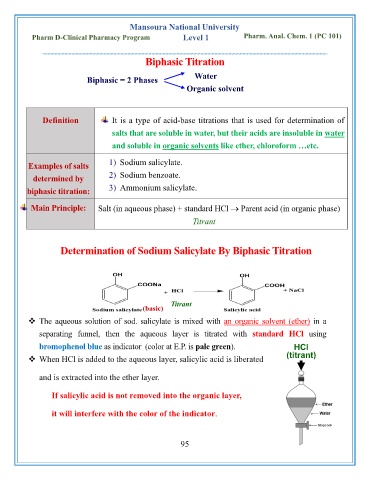
Biphasic Titration
Biphasic = 2 Phases Water
Organic solvent
Definition It is a type of acid-base titrations that is used for determination of
salts that are soluble in water, but their acids are insoluble in water
and soluble in organic solvents like ether, chloroform …etc.
Examples of salts 1) Sodium salicylate.
determined by 2) Sodium benzoate.
biphasic titration: 3) Ammonium salicylate.
Main Principle: Salt (in aqueous phase) + standard HCl → Parent acid (in organic phase)
Titrant
Determination of Sodium Salicylate By Biphasic Titration
(basic) Titrant
❖ The aqueous solution of sod. salicylate is mixed with an organic solvent (ether) in a
separating funnel, then the aqueous layer is titrated with standard HCl using
bromophenol blue as indicator (color at E.P. is pale green). HCl
(titrant)
❖ When HCl is added to the aqueous layer, salicylic acid is liberated
and is extracted into the ether layer.
If salicylic acid is not removed into the organic layer,
it will interfere with the color of the indicator.
95