Page 6 - UVSpecPaperBDASWhitePaperandBMGLabTechNote
P. 6
(17) though provide references here detailing the use of with another research group in the near future. The
other instruments including those dedicated simply to evaluation and assessment of many more beverages are
distilled spirits authenticity testing and product quality now possible through the use of UV-visible spectroscopy.
evaluations. One key advantage with micro-well plate Such results will impact quality, safety, the collection of
reading is the ability to ensure a narrow path length via taxes and a reduction in economic losses to the industry
small volume sample addition. In other instruments through detection of fake and adulterated products in
there is sometimes a need to switch path-length devices the marketplace and possibly via “authentic seals of
which may slow down analysis time. In addition only a approval” via regulatory testing bodies. Application
single sample can be tested via pumping sample through of the technique in analyzing competitor samples and
such units. product formulation are also possible through this
methodology. Rapid aging for measuring deterioration
Regardless as to single or multiple analyses at one time of quality or rapid aging/maturation of spirits may
the ability to test many types and styles of beverages is also be examined via “fingerprinting” and monitoring
the main aim of our short discourse here; providing what changes in Maillard reaction components (for example)
we feel to be an important introduction to the industry. and “bleaching” of samples as noted by specific regional
The reader will be able to evaluate the advantages and peak and shoulder changes (unpublished observations
disadvantages of each type of instrument as it applies to and see below).
their specific needs and situation. The literature on this
topic is limited and largely represented in our reference Results and Conclusions Typical data for a range of
list. This literature will, however, hopefully assist both distilled spirits – white or raw un-aged spirits and aged
the beverage manufacturer in assessing the scope of this (usually exhibiting color derived during maturation)
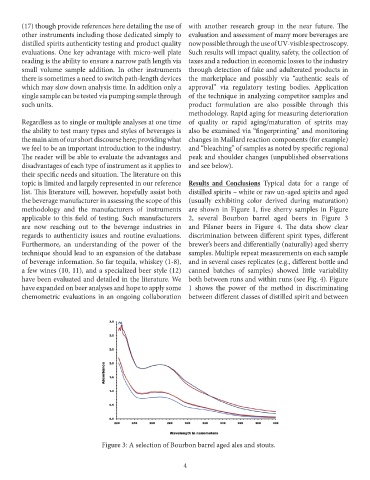
methodology and the manufacturers of instruments are shown in Figure 1, five sherry samples in Figure
applicable to this field of testing. Such manufacturers 2, several Bourbon barrel aged beers in Figure 3
are now reaching out to the beverage industries in and Pilsner beers in Figure 4. The data show clear
regards to authenticity issues and routine evaluations. discrimination between different spirit types, different
Furthermore, an understanding of the power of the brewer’s beers and differentially (naturally) aged sherry
technique should lead to an expansion of the database samples. Multiple repeat measurements on each sample
of beverage information. So far tequila, whiskey (1-8), and in several cases replicates (e.g., different bottle and
a few wines (10, 11), and a specialized beer style (12) canned batches of samples) showed little variability
have been evaluated and detailed in the literature. We both between runs and within runs (see Fig. 4). Figure
have expanded on beer analyses and hope to apply some 1 shows the power of the method in discriminating
chemometric evaluations in an ongoing collaboration between different classes of distilled spirit and between
Figure 3: A selection of Bourbon barrel aged ales and stouts.
4