Page 160 - Fundamentals of Management Myths Debunked (2017)_Flat
P. 160
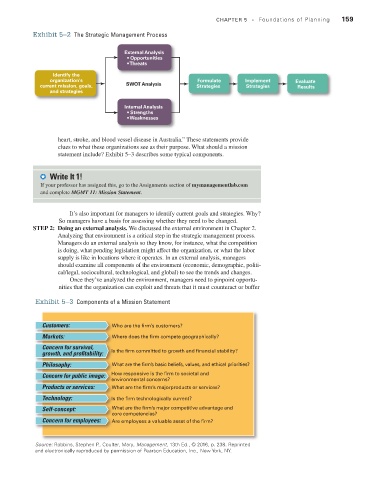
Exhibit 5–2 The Strategic Management Process CHAPTER 5 • Foundations of Planning 159
External Analysis
• Opportunities
• Threats
Identify the
organization's Formulate Implement Evaluate
current mission, goals, SWOT Analysis Strategies Strategies Results
and strategies
Internal Analysis
• Strengths
• Weaknesses
heart, stroke, and blood vessel disease in Australia.” These statements provide
clues to what these organizations see as their purpose. What should a mission
statement include? Exhibit 5–3 describes some typical components.
Write It 1!
If your professor has assigned this, go to the Assignments section of mymanagementlab.com
and complete MGMT 11: Mission Statement.
It’s also important for managers to identify current goals and strategies. Why?
So managers have a basis for assessing whether they need to be changed.
Step 2: Doing an external analysis. We discussed the external environment in Chapter 2.
Analyzing that environment is a critical step in the strategic management process.
Managers do an external analysis so they know, for instance, what the competition
is doing, what pending legislation might affect the organization, or what the labor
supply is like in locations where it operates. In an external analysis, managers
should examine all components of the environment (economic, demographic, politi-
cal/legal, sociocultural, technological, and global) to see the trends and changes.
Once they’ve analyzed the environment, managers need to pinpoint opportu-
nities that the organization can exploit and threats that it must counteract or buffer
Exhibit 5–3 Components of a Mission Statement
Customers: Who are the firm’s customers?
Markets: Where does the firm compete geographically?
Concern for survival,
Is the rm committed to growth and nancial stability?
growth, and profitability:
Philosophy: What are the firm’s basic beliefs, values, and ethical priorities?
Concern for public image: How responsive is the firm to societal and
environmental concerns?
Products or services: What are the firm’s majorproducts or services?
Technology: Is the firm technologically current?
Self-concept: What are the firm’s major competitive advantage and
core competencies?
Concern for employees: Are employees a valuable asset of the firm?
Source: Robbins, Stephen P., Coulter, Mary, Management, 13th Ed., © 2016, p. 238. Reprinted
and electronically reproduced by permission of Pearson Education, Inc., New York, NY.