Page 452 - Fundamentals of Management Myths Debunked (2017)_Flat
P. 452
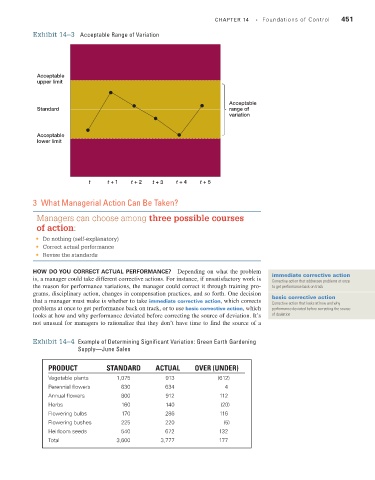
Exhibit 14–3 Acceptable Range of Variation CHAPTER 14 • Foundations of Control 451
Acceptable
upper limit
•
• • Acceptable
Standard range of
• variation
•
Acceptable •
lower limit
t t + 1 t + 2 t + 3 t + 4 t + 5
3 What Managerial Action Can Be Taken?
Managers can choose among three possible courses
of action:
• Do nothing (self-explanatory)
• Correct actual performance
• Revise the standards
How Do You CorreCt aCtual PerforManCe? Depending on what the problem immediate corrective action
is, a manager could take different corrective actions. For instance, if unsatisfactory work is Corrective action that addresses problems at once
the reason for performance variations, the manager could correct it through training pro- to get performance back on track
grams, disciplinary action, changes in compensation practices, and so forth. One decision basic corrective action
that a manager must make is whether to take immediate corrective action, which corrects Corrective action that looks at how and why
problems at once to get performance back on track, or to use basic corrective action, which performance deviated before correcting the source
looks at how and why performance deviated before correcting the source of deviation. It’s of deviation
not unusual for managers to rationalize that they don’t have time to find the source of a
Exhibit 14–4 Example of Determining Significant Variation: Green Earth Gardening
Supply—June Sales
ProduCt Standard aCtual over (under)
Vegetable plants 1,075 913 (612)
Perennial flowers 630 634 4
Annual flowers 800 912 112
Herbs 160 140 (20)
Flowering bulbs 170 286 116
Flowering bushes 225 220 (5)
Heirloom seeds 540 672 132
Total 3,600 3,777 177