Page 110 - Krugmans Economics for AP Text Book_Neat
P. 110
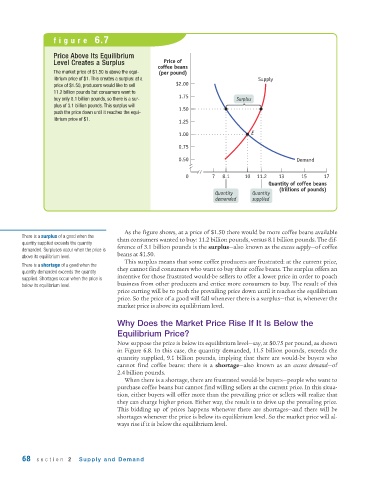
figure 6.7
Price Above Its Equilibrium
Level Creates a Surplus Price of
coffee beans
The market price of $1.50 is above the equi- (per pound)
librium price of $1. This creates a surplus: at a Supply
price of $1.50, producers would like to sell $2.00
11.2 billion pounds but consumers want to
buy only 8.1 billion pounds, so there is a sur- 1.75 Surplus
plus of 3.1 billion pounds. This surplus will 1.50
push the price down until it reaches the equi-
librium price of $1. 1.25
1.00 E
0.75
0.50 Demand
0 7 8.1 10 11.2 13 15 17
Quantity of coffee beans
(billions of pounds)
Quantity Quantity
demanded supplied
As the figure shows, at a price of $1.50 there would be more coffee beans available
There is a surplus of a good when the
than consumers wanted to buy: 11.2 billion pounds, versus 8.1 billion pounds. The dif-
quantity supplied exceeds the quantity
ference of 3.1 billion pounds is the surplus—also known as the excess supply—of coffee
demanded. Surpluses occur when the price is
beans at $1.50.
above its equilibrium level.
This surplus means that some coffee producers are frustrated: at the current price,
There is a shortage of a good when the
they cannot find consumers who want to buy their coffee beans. The surplus offers an
quantity demanded exceeds the quantity
incentive for those frustrated would-be sellers to offer a lower price in order to poach
supplied. Shortages occur when the price is
below its equilibrium level. business from other producers and entice more consumers to buy. The result of this
price cutting will be to push the prevailing price down until it reaches the equilibrium
price. So the price of a good will fall whenever there is a surplus—that is, whenever the
market price is above its equilibrium level.
Why Does the Market Price Rise If It Is Below the
Equilibrium Price?
Now suppose the price is below its equilibrium level—say, at $0.75 per pound, as shown
in Figure 6.8. In this case, the quantity demanded, 11.5 billion pounds, exceeds the
quantity supplied, 9.1 billion pounds, implying that there are would-be buyers who
cannot find coffee beans: there is a shortage—also known as an excess demand—of
2.4 billion pounds.
When there is a shortage, there are frustrated would-be buyers—people who want to
purchase coffee beans but cannot find willing sellers at the current price. In this situa-
tion, either buyers will offer more than the prevailing price or sellers will realize that
they can charge higher prices. Either way, the result is to drive up the prevailing price.
This bidding up of prices happens whenever there are shortages—and there will be
shortages whenever the price is below its equilibrium level. So the market price will al-
ways rise if it is below the equilibrium level.
68 section 2 Supply and Demand