Page 355 - Krugmans Economics for AP Text Book_Neat
P. 355
fyi
What the Fed Wants, the Fed Gets
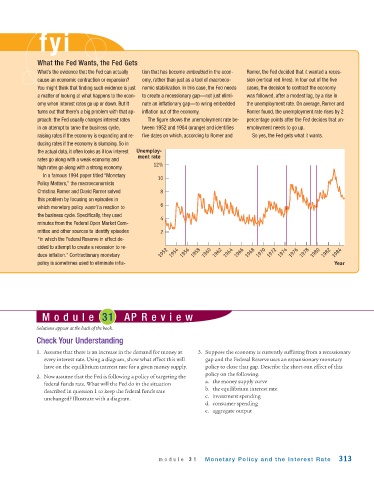
What’s the evidence that the Fed can actually tion that has become embedded in the econ- Romer, the Fed decided that it wanted a reces-
cause an economic contraction or expansion? omy, rather than just as a tool of macroeco- sion (vertical red lines). In four out of the five
You might think that finding such evidence is just nomic stabilization. In this case, the Fed needs cases, the decision to contract the economy
a matter of looking at what happens to the econ- to create a recessionary gap—not just elimi- was followed, after a modest lag, by a rise in
omy when interest rates go up or down. But it nate an inflationary gap—to wring embedded the unemployment rate. On average, Romer and
turns out that there’s a big problem with that ap- inflation out of the economy. Romer found, the unemployment rate rises by 2
proach: the Fed usually changes interest rates The figure shows the unemployment rate be- percentage points after the Fed decides that un-
in an attempt to tame the business cycle, tween 1952 and 1984 (orange) and identifies employment needs to go up.
raising rates if the economy is expanding and re- five dates on which, according to Romer and So yes, the Fed gets what it wants.
ducing rates if the economy is slumping. So in
the actual data, it often looks as if low interest Unemploy-
ment rate
rates go along with a weak economy and
12%
high rates go along with a strong economy.
In a famous 1994 paper titled “Monetary
10
Policy Matters,” the macroeconomists
Christina Romer and David Romer solved 8
this problem by focusing on episodes in
6
which monetary policy wasn’t a reaction to
the business cycle. Specifically, they used
4
minutes from the Federal Open Market Com-
mittee and other sources to identify episodes 2
“in which the Federal Reserve in effect de-
cided to attempt to create a recession to re-
duce inflation.” Contractionary monetary 1952 1954 1956 1958 1960 1962 1964 1966 1968 1970 1972 1974 1976 1978 1980 1982 1984
policy is sometimes used to eliminate infla- Year
Module 31 AP Review
Solutions appear at the back of the book.
Check Your Understanding
1. Assume that there is an increase in the demand for money at 3. Suppose the economy is currently suffering from a recessionary
every interest rate. Using a diagram, show what effect this will gap and the Federal Reserve uses an expansionary monetary
have on the equilibrium interest rate for a given money supply. policy to close that gap. Describe the short -run effect of this
policy on the following.
2. Now assume that the Fed is following a policy of targeting the
a. the money supply curve
federal funds rate. What will the Fed do in the situation
b. the equilibrium interest rate
described in question 1 to keep the federal funds rate
c. investment spending
unchanged? Illustrate with a diagram.
d. consumer spending
e. aggregate output
module 31 Monetary Policy and the Interest Rate 313