Page 630 - Krugmans Economics for AP Text Book_Neat
P. 630
To see how these curves can be used to decide whether production is profitable or
unprofitable, recall that profit is equal to total revenue minus total cost, TR − TC.
This means:
■ If the firm produces a quantity at which TR > TC, the firm is profitable.
■ If the firm produces a quantity at which TR = TC, the firm breaks even.
■ If the firm produces a quantity at which TR < TC, the firm incurs a loss.
We can also express this idea in terms of revenue and cost per unit of output. If we
divide profit by the number of units of output, Q, we obtain the following expression
for profit per unit of output:
(58-1) Profit/Q = TR/Q − TC/Q
TR/Q is average revenue, which is the market price. TC/Q is average total cost. So a
firm is profitable if the market price for its product is more than the average total cost
of the quantity the firm produces; a firm experiences losses if the market price is less
than the average total cost of the quantity the firm produces. This means:
■ If the firm produces a quantity at which P > ATC, the firm is profitable.
■ If the firm produces a quantity at which P = ATC, the firm breaks even.
■ If the firm produces a quantity at which P < ATC, the firm incurs a loss.
In summary, in the short run a firm will maximize profit by producing the quan-
tity of output at which MC = MR. A perfectly competitive firm is a price-taker, so it
can sell as many units of output as it would like at the market price. This means that
for a perfectly competitive firm it is always true that MR = P. The firm is profitable, or
breaks even, as long as the market price is greater than, or equal to, average total cost.
In the next module, we develop the perfect competition model using graphs to ana-
lyze the firm’s level of profit.
Module 58 AP Review
Solutions appear at the back of the book.
Check Your Understanding
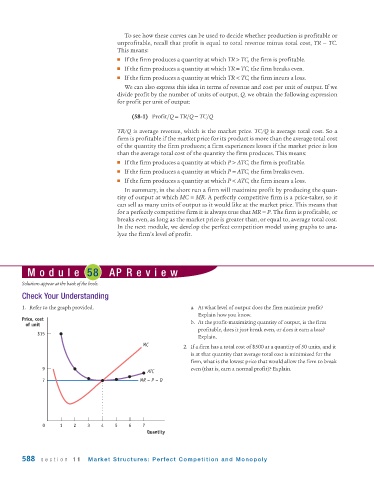
1. Refer to the graph provided. a. At what level of output does the firm maximize profit?
Explain how you know.
Price, cost
of unit b. At the profit-maximizing quantity of output, is the firm
profitable, does it just break even, or does it earn a loss?
$15
Explain.
MC
2. If a firm has a total cost of $500 at a quantity of 50 units, and it
is at that quantity that average total cost is minimized for the
firm, what is the lowest price that would allow the firm to break
9 even (that is, earn a normal profit)? Explain.
ATC
7 MR = P = D
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
Quantity
588 section 11 Market Structures: Perfect Competition and Monopoly