Page 819 - Krugmans Economics for AP Text Book_Neat
P. 819
Section 14 Summary
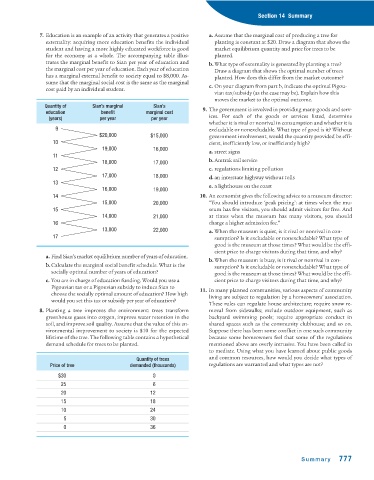
7. Education is an example of an activity that generates a positive a. Assume that the marginal cost of producing a tree for
externality: acquiring more education benefits the individual planting is constant at $20. Draw a diagram that shows the
student and having a more highly educated workforce is good market equilibrium quantity and price for trees to be
for the economy as a whole. The accompanying table illus- planted.
trates the marginal benefit to Sian per year of education and b.What type of externality is generated by planting a tree?
the marginal cost per year of education. Each year of education Draw a diagram that shows the optimal number of trees
has a marginal external benefit to society equal to $8,000. As- planted. How does this differ from the market outcome?
sume that the marginal social cost is the same as the marginal
c. On your diagram from part b, indicate the optimal Pigou-
cost paid by an individual student.
vian tax/subsidy (as the case may be). Explain how this
moves the market to the optimal outcome.
Quantity of Sian’s marginal Sian’s 9. The government is involved in providing many goods and serv-
education benefit marginal cost
(years) per year per year ices. For each of the goods or services listed, determine
whether it is rival or nonrival in consumption and whether it is
9 excludable or nonexcludable. What type of good is it? Without
$20,000 $15,000 government involvement, would the quantity provided be effi-
10 cient, inefficiently low, or inefficiently high?
19,000 16,000
a. street signs
11
18,000 17,000 b.Amtrak rail service
12 c. regulations limiting pollution
17,000 18,000 d.an interstate highway without tolls
13 e. a lighthouse on the coast
16,000 19,000
14 10. An economist gives the following advice to a museum director:
15,000 20,000 “You should introduce ‘peak pricing’: at times when the mu-
15 seum has few visitors, you should admit visitors for free. And
14,000 21,000 at times when the museum has many visitors, you should
16 charge a higher admission fee.”
13,000 22,000 a. When the museum is quiet, is it rival or nonrival in con-
17 sumption? Is it excludable or nonexcludable? What type of
good is the museum at those times? What would be the effi-
cient price to charge visitors during that time, and why?
a. Find Sian’s market equilibrium number of years of education.
b.When the museum is busy, is it rival or nonrival in con-
b.Calculate the marginal social benefit schedule. What is the sumption? Is it excludable or nonexcludable? What type of
socially optimal number of years of education? good is the museum at those times? What would be the effi-
c. You are in charge of education funding. Would you use a cient price to charge visitors during that time, and why?
Pigouvian tax or a Pigouvian subsidy to induce Sian to
11. In many planned communities, various aspects of community
choose the socially optimal amount of education? How high
living are subject to regulation by a homeowners’ association.
would you set this tax or subsidy per year of education?
These rules can regulate house architecture; require snow re-
8. Planting a tree improves the environment: trees transform moval from sidewalks; exclude outdoor equipment, such as
greenhouse gases into oxygen, improve water retention in the backyard swimming pools; require appropriate conduct in
soil, and improve soil quality. Assume that the value of this en- shared spaces such as the community clubhouse; and so on.
vironmental improvement to society is $10 for the expected Suppose there has been some conflict in one such community
lifetime of the tree. The following table contains a hypothetical because some homeowners feel that some of the regulations
demand schedule for trees to be planted. mentioned above are overly intrusive. You have been called in
to mediate. Using what you have learned about public goods
Quantity of trees and common resources, how would you decide what types of
Price of tree demanded (thousands) regulations are warranted and what types are not?
$30 0
25 6
20 12
15 18
10 24
5 30
0 36
Summary 777