Page 883 - Krugmans Economics for AP Text Book_Neat
P. 883
S-37
SOLUTIONS TO AP REVIEW QUESTIONS
3. b generating an increase in supply, a fall in price, and a
4. d fall in profits. Once profits are driven back to zero,
entry will cease.
5. c d. The shortage of a key input causes that input’s price
to increase, resulting in an increase in average variable
Tackle the Test: and average total cost for producers. Firms incur losses
Free-Response Questions in the short run, and some firms will exit the industry
in the long run. The fall in supply generates an
2. a. 6
increase in price and decreased losses. Exit will cease
b. $20 × 6 = $120 when the losses for remaining firms have returned
c. $29.50 × 6 = $177 to zero.
d. $120 − $177 =−$57 (or a loss of $57) 2.
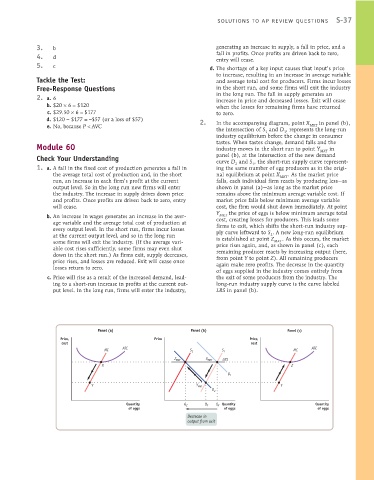
e. No, because P < AVC In the accompanying diagram, point X MKT in panel (b),
the intersection of S and D , represents the long-run
1 1
industry equilibrium before the change in consumer
Module 60 tastes. When tastes change, demand falls and the
industry moves in the short run to point Y
in
MKT
Check Your Understanding panel (b), at the intersection of the new demand
curve D and S , the short-run supply curve represent-
2
1
1. a. A fall in the fixed cost of production generates a fall in ing the same number of egg producers as in the origi-
the average total cost of production and, in the short nal equilibrium at point X MKT . As the market price
run, an increase in each firm’s profit at the current falls, each individual firm reacts by producing less—as
output level. So in the long run new firms will enter shown in panel (a)—as long as the market price
the industry. The increase in supply drives down price remains above the minimum average variable cost. If
and profits. Once profits are driven back to zero, entry market price falls below minimum average variable
will cease. cost, the firm would shut down immediately. At point
Y the price of eggs is below minimum average total
MKT
b. An increase in wages generates an increase in the aver- cost, creating losses for producers. This leads some
age variable and the average total cost of production at
firms to exit, which shifts the short-run industry sup-
every output level. In the short run, firms incur losses ply curve leftward to S . A new long-run equilibrium
at the current output level, and so in the long run 2
is established at point Z . As this occurs, the market
MKT
some firms will exit the industry. (If the average vari- price rises again, and, as shown in panel (c), each
able cost rises sufficiently, some firms may even shut
remaining producer reacts by increasing output (here,
down in the short run.) As firms exit, supply decreases, from point Y to point Z). All remaining producers
price rises, and losses are reduced. Exit will cease once
again make zero profits. The decrease in the quantity
losses return to zero.
of eggs supplied in the industry comes entirely from
c. Price will rise as a result of the increased demand, lead- the exit of some producers from the industry. The
ing to a short-run increase in profits at the current out- long-run industry supply curve is the curve labeled
put level. In the long run, firms will enter the industry, LRS in panel (b).
Panel (a) Panel (b) Panel (c)
Price, Price Price,
cost cost
ATC ATC
MC S 2 S 1 MC
Z MKT X MKT LRS
X Z
D 1
Y Y MKT Y
D 2
Quantity Q Z Q Y Q X Quantity Quantity
of eggs of eggs of eggs
Decrease in
output from exit