Page 24 - ASOP ROT Study Guide
P. 24
Ligaments are composed of collagen fibers arranged in more or less parallel bundles. They are
attached to the bones on either side of a joint, holding the joint in place and resisting stretching
forces pulling on the joints, thus providing joint stability. The position of the ligaments around a
joint determines the direction in which the joint can move. They determine the axis of motion of a
joint by limiting the directions in which it may move. Ligaments have a blood supply and a nerve
supply. They have no regenerative powers so if they are damaged they heal by repair, forming a
scar. The scar is unlikely to result in healing at the correct length, and scar tissue is liable to
stretch under tension. Therefore the healing of ligaments quite often leaves a less efficient
structure than the original one. If the sensory receptors and nerves in a ligament are damaged this
can cause the loss of the ability to provide the central nervous system with accurate sensory
information. The loss of sensory information is particularly serious as this prevents the reflex
contractions of antagonist muscles to protect a joint from abnormal loads or from being place in
unsatisfactory positions.
4 . 6 Menisci
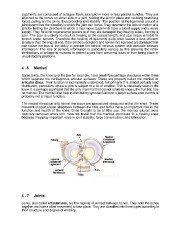
Some joints, the knee and the jaw for example, have small fibrocartilage structures within them
which separate the cartilaginous articular surfaces. These are properly called the menisci or
articular discs. Their function is incompletely understood, but primarily it is almost certainly load
distribution, particularly where a joint is subject to a lot of rotation. This is classically seen in the
knee. It is perhaps significant that the only mammal that cannot rotate its knees, the fruit bat, has
no menisci. The menisci also help in distributing synovial fluid over a larger surface area but this is
probably not a major function.
The medial meniscus and lateral meniscus are specialized structures within the knee. These
crescent-shaped shock absorbers between the tibia and femur have an important role in the
function and health of the knee. Once thought to be of little use, the menisci (plural) were
routinely removed when torn. Now we know that the menisci contribute to a healthy knee
because they play important roles in joint stability, force transmission, and lubrication.
4 . 7 Joints
Joints, also called articulations, are the regions of contact between bones. They hold the bones
together and some allow movement to take place. They are classified into three types according to
their structure and degree of mobility.