Page 52 - ASOP ROT Study Guide
P. 52
ttp://www.totum.ca/other-pages/knee-injuries/
For example if a collateral ligament is ruptured the knee can still be quite stable, especially in the
straight position. On the other hand an accident, such as a lateral blow to the leg, will often
damage more than one ligament, and in this case the knee is not stable.
Muscles have a minor role in controlling stability at the knee. The muscle with most relevance is
probably the extensor muscle (quadriceps). If this is weak the patient may feel a loss of stability at
the knee and the knee may be more prone to injury. Also during rehabilitation following knee
injuries a patient may be required to do exercises to strengthen the quadriceps. This can give some
compensation for the stability lost by permanent ligament or meniscus damage.
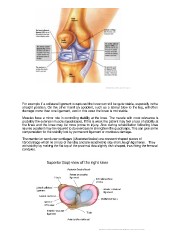
The menisci or semilunar cartilages ((illustrated below) are crescent shaped pieces of
fibrocartilage which lie on top of the tibia and are attached to it by short, tough ligaments. They
aid stability by making the flat top of the proximal tibia slightly dish shaped, thus fitting the femoral
condyles.
hnthebodyman.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/07/Menisci-of-human-knee-top-view.jpg