Page 14 - RemoteSnsing&GIS by PK Gogoi
P. 14
10
9
can easily reach on the earth’s surface.These are he specular or mirror-like reflection occurs maximum chlorophyll and thus, it reflects more
the portions of EMR having different Tover the surface of smooth topography, like green. But, on the contrary, during autumn, tree
wavelengths,and not blocked by any our National Highways, where all (or almost all) leaves produce less chlorophyll ,and reflecting
atmospheric elements in the atmosphere.These of the energy is directed away from the surface the red wavelengths. Thus it appears red or
unblocked portions of EMR or spectrum is in a single direction. On the other hand, Diffuse yellow (yellow is a combination of red and green
called ‘atmospheric windows’. The visible reflection occurs when the surface is rough and wavelengths).It is to be further added that all
portion of the spectrum, to which our eyes are the energy is reflected almost uniformly in all healthy trees having green leaves can reflect
most sensitive, corresponds to both an near-infrared wavelengths. By observing the IR
atmospheric window and the peak energy level of the earth , and condition of the feature. The reflectance from trees ,scientists can determine
of the sun. equation of incident rays is expressed as EI (l) health(lavishness) of vegetation cover.
nergy emitted by the Earth corresponds = EA (l) + ET (l) + ER(l) where, EI(I) = n remote sensing, due to interaction of
Eto a window around 10 um in the thermal Indecent Ebergy, EA= Absorbed Energy , ET IIncidence ray(I) with that of the target (T),-
IR portion of the spectrum. Keeping in view of Transmitted Energy and ER Radiated Energy that is the earth’s lithosphere - transfers EMR
the such atmospheric windows of spectrum ,
remote sensing sensors are designed for
acquiring data. directions. The nature of reflection, therefore,
depends on the nature of topography of the
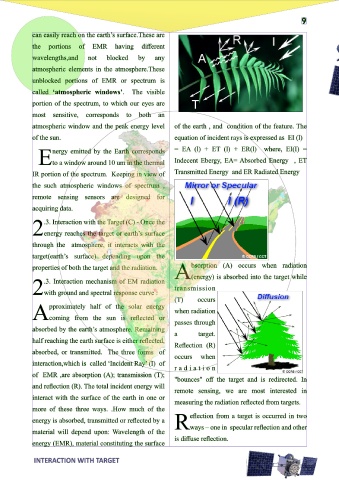
.3. Interaction with the Target (C) - Once the
earth’s features.Whether a particular target
2energy reaches the target or earth’s surface
reflects ‘specularly’ or ‘diffusely’, or
through the atmosphere, it interacts with the
somewhere in between, depends on the surface
target(earth’s surface) depending upon the
properties of both the target and the radiation. bsorption (A) occurs when radiation roughness of the feature in comparison to the
A(energy) is absorbed into the target while wavelength of the incoming radiation. If the
.3. Interaction mechanism of EM radiation
transmission wavelengths are much smaller than the particle
2with ground and spectral response curve :
(T) occurs sizes of the earth’s features, then from the
pproximately half of the solar energy terrestrial surface, diffuse reflection will occur.In
when radiation
Acoming from the sun is reflected or viewing remote sensing imageries it may either
passes through
absorbed by the earth’s atmosphere. Remaining be appeared smooth to long wavelength
a target.
half reaching the earth surface is either reflected, microwaves, or be appeared quite rough to the
Reflection (R)
absorbed, or transmitted. The three forms of visible wavelengths.
occurs when
interaction,which is called ‘Incident Ray’ (I) of
r a d i a t i o n hlorophyll, presents in the leaves of energy through the features of the earth and
of EMR ,are absorption (A); transmission (T);
"bounces" off the target and is redirected. In Cplant, absorb radiation of the red and subsequently, ire-radiates back to the
and reflection (R). The total incident energy will
remote sensing, we are most interested in blue wavelengths almost completely but reflects atmosphere in the form of long -wave terrestrial
interact with the surface of the earth in one or
measuring the radiation reflected from targets. its green wavelengths. That is why leaves radiation. In the following paragraph, a pictorial
more of these three ways. .How much of the
eflection from a target is occurred in two appear ‘green’. There is a variation of reflected representation of energy reflectance of different
energy is absorbed, transmitted or reflected by a
Rways – one in specular reflection and other colour from the leaves from season to objects will be discussed.
material will depend upon: Wavelength of the
is diffuse reflection. season.During summer, plant leaves produces
energy (EMR), material constituting the surface