Page 120 - PG 504-theoretical notes-phyto-1-2024-2025..
P. 120
Clinical pharmacy PharmD program Third level Phytochemistry-1 (PG-504)
It does not dissolve but only deacetylated to yield acetic acid and chitosan.
Only deacetylated → Chitosan + Acetic acid
2) Chitosan
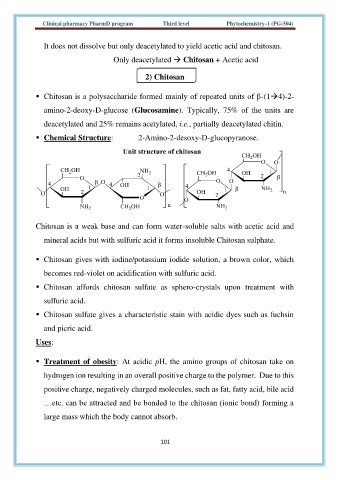
▪ Chitosan is a polysaccharide formed mainly of repeated units of β-(1→4)-2-
amino-2-deoxy-D-glucose (Glucosamine). Typically, 75% of the units are
deacetylated and 25% remains acetylated, i.e., partially deacetylated chitin.
▪ Chemical Structure: 2-Amino-2-desoxy-D-glucopyranose.
Chitosan is a weak base and can form water-soluble salts with acetic acid and
mineral acids but with sulfuric acid it forms insoluble Chitosan sulphate.
▪ Chitosan gives with iodine/potassium iodide solution, a brown color, which
becomes red-violet on acidification with sulfuric acid.
▪ Chitosan affords chitosan sulfate as sphero-crystals upon treatment with
sulfuric acid.
▪ Chitosan sulfate gives a characteristic stain with acidic dyes such as fuchsin
and picric acid.
Uses:
▪ Treatment of obesity: At acidic pH, the amino groups of chitosan take on
hydrogen ion resulting in an overall positive charge to the polymer. Due to this
positive charge, negatively charged molecules, such as fat, fatty acid, bile acid
…etc. can be attracted and be bonded to the chitosan (ionic bond) forming a
large mass which the body cannot absorb.
101