Page 123 - PG 504-theoretical notes-phyto-1-2024-2025..
P. 123
Clinical pharmacy PharmD program Third level Phytochemistry-1 (PG-504)
Functions: In cartilage, it binds collagen & hold fibers in a tight strong
network.
Role in Compressibility of cartilage in weight bearing.
Used in the management of osteoarthritis symptoms
Heparin
Occurrence: The main sources of commercial heparin are: lung and liver
tissues.
Functions: It is an anticoagulant (prevents blood clotting), administered
intravenously.
• When released into the blood, it inhibits clot formation by interacting with the
protein antithrombin.
• If hemorrhage occurs, the anticoagulant effects of heparin can be reversed in
minutes by the administration of protamine sulfate
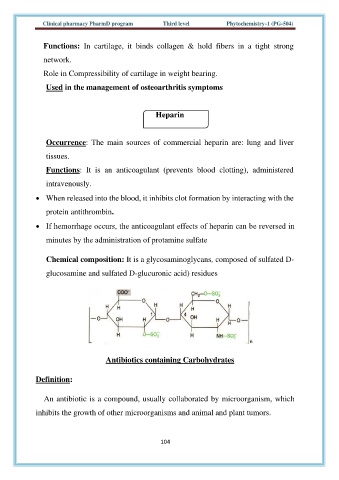
Chemical composition: It is a glycosaminoglycans, composed of sulfated D-
glucosamine and sulfated D-glucuronic acid) residues
Antibiotics containing Carbohydrates
Definition:
An antibiotic is a compound, usually collaborated by microorganism, which
inhibits the growth of other microorganisms and animal and plant tumors.
104