Page 26 - SE Outlook Regions 2022
P. 26
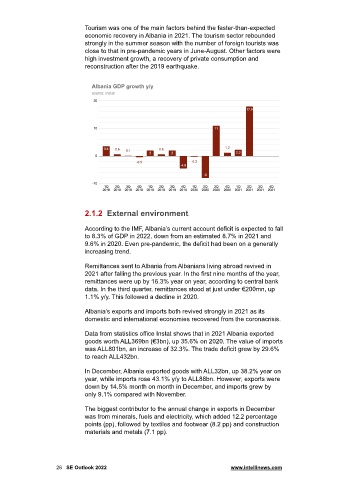
Tourism was one of the main factors behind the faster-than-expected
economic recovery in Albania in 2021. The tourism sector rebounded
strongly in the summer season with the number of foreign tourists was
close to that in pre-pandemic years in June-August. Other factors were
high investment growth, a recovery of private consumption and
reconstruction after the 2019 earthquake.
2.1.2 External environment
According to the IMF, Albania’s current account deficit is expected to fall
to 8.3% of GDP in 2022, down from an estimated 8.7% in 2021 and
9.6% in 2020. Even pre-pandemic, the deficit had been on a generally
increasing trend.
Remittances sent to Albania from Albanians living abroad revived in
2021 after falling the previous year. In the first nine months of the year,
remittances were up by 16.3% year on year, according to central bank
data. In the third quarter, remittances stood at just under €200mn, up
1.1% y/y. This followed a decline in 2020.
Albania’s exports and imports both revived strongly in 2021 as its
domestic and international economies recovered from the coronacrisis.
Data from statistics office Instat shows that in 2021 Albania exported
goods worth ALL369bn (€3bn), up 35.6% on 2020. The value of imports
was ALL801bn, an increase of 32.3%. The trade deficit grew by 29.6%
to reach ALL432bn.
In December, Albania exported goods with ALL32bn, up 38.2% year on
year, while imports rose 43.1% y/y to ALL88bn. However, exports were
down by 14.5% month on month in December, and imports grew by
only 9.1% compared with November.
The biggest contributor to the annual change in exports in December
was from minerals, fuels and electricity, which added 12.2 percentage
points (pp), followed by textiles and footwear (8.2 pp) and construction
materials and metals (7.1 pp).
26 SE Outlook 2022 www.intellinews.com