Page 6 - FSUOGM Week 15 2022
P. 6
FSUOGM COMMENTARY FSUOGM
countries of the Netherlands, Germany, Poland the crude is important, as a low sulphur content
and Italy receiving the next 30%. German refin- means a fuel that produces less GHG emissions.
eries in particular are heavily dependent on
Russian crude and directly connected to Russian German refineries
oilfields via the Druzhba pipelines. Oil consumption is still Germany’s most impor-
China is the world's top importer of Russian tant primary energy source, although it has been
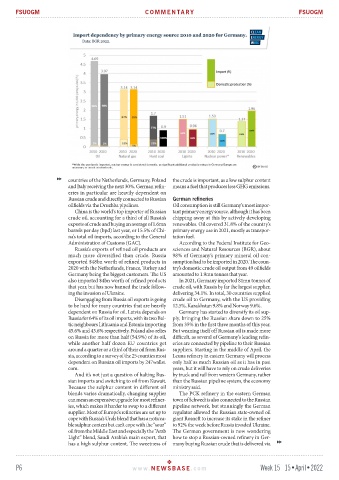
crude oil, accounting for a third of all Russia’s chipping away at this by actively developing
exports of crude and buying an average of 1.6mn renewables. Oil covered 31.8% of the country’s
barrels per day (bpd) last year, or 15.5% of Chi- primary energy use in 2021, mostly as transpor-
na’s total oil imports, according to the General tation fuel.
Administration of Customs (GAC). According to the Federal Institute for Geo-
Russia’s exports of refined oil products are sciences and Natural Resources (BGR), about
much more diversified than crude. Russia 98% of Germany’s primary mineral oil con-
exported $48bn worth of refined products in sumption had to be imported in 2020. The coun-
2020 with the Netherlands, France, Turkey and try’s domestic crude oil output from 49 oilfields
Germany being the biggest customers. The US amounted to 1.9mn tonnes that year.
also imported $4bn worth of refined products In 2021, Germany imported 81mn tonnes of
that year, but has now banned the trade follow- crude oil, with Russia by far the largest supplier,
ing the invasion of Ukraine. delivering 34.1%. In total, 30 countries supplied
Disengaging from Russia oil exports is going crude oil to Germany, with the US providing
to be hard for many countries that are heavily 12.5%, Kazakhstan 9.8% and Norway 9.6%.
dependent on Russia for oil. Latvia depends on Germany has started to diversify its oil sup-
Russia for 64% of its oil imports, with its two Bal- ply, bringing the Russian share down to 25%
tic neighbours Lithuania and Estonia importing from 35% in the first three months of this year.
45.6% and 43.6% respectively. Poland also relies But weaning itself off Russian oil is made more
on Russia for more than half (54.9%) of its oil, difficult, as several of Germany’s leading refin-
while another half dozen EU countries get eries are connected by pipeline to their Russian
around a quarter or a third of their oil from Rus- suppliers. Starting in the middle of April, the
sia, according to a survey of the 25 counties most Leuna refinery in eastern Germany will process
dependent on Russian oil imports by 247wallst. only half as much Russian oil as it has in past
com. years, but it will have to rely on crude deliveries
And it’s not just a question of halting Rus- by truck and rail from western Germany, rather
sian imports and switching to oil from Kuwait. than the Russian pipeline system, the economy
Because the sulphur content in different oil ministry said.
blends varies dramatically, changing supplier The PCK refinery in the eastern German
can mean an expensive upgrade for most refiner- town of Schwedt is also connected to the Russian
ies, which makes it harder to swap to a different pipeline network, but stunningly the German
supplier. Most of Europe’s refineries are set up to regulator allowed the Russian state-owned oil
cope with Russia’s Urals blend that has a noticea- giant Rosneft to increase its stake in the refiner
ble sulphur content but can’t cope with the “sour” to 92% the week before Russia invaded Ukraine.
oil from the Middle East and especially the “Arab The German government is now wondering
Light” blend, Saudi Arabia’s main export, that how to stop a Russian-owned refinery in Ger-
has a high sulphur content. The sweetness of many buying Russian crude that is delivered via
P6 www. NEWSBASE .com Week 15 15•April•2022