Page 25 - PHLEBOTOMY STUDY GUIDE
P. 25
Page 25 of 36
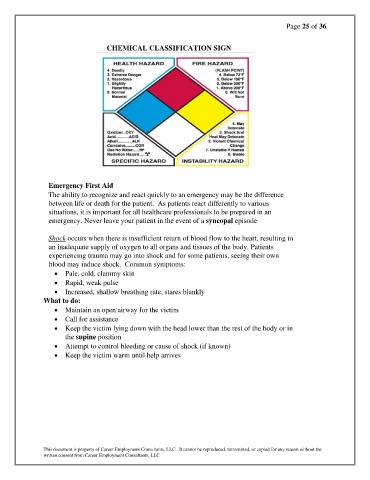
CHEMICAL CLASSIFICATION SIGN
Emergency First Aid
The ability to recognize and react quickly to an emergency may be the difference
between life or death for the patient. As patients react differently to various
situations, it is important for all healthcare professionals to be prepared in an
emergency. Never leave your patient in the event of a syncopal episode
Shock occurs when there is insufficient return of blood flow to the heart, resulting in
an inadequate supply of oxygen to all organs and tissues of the body. Patients
experiencing trauma may go into shock and for some patients, seeing their own
blood may induce shock. Common symptoms:
• Pale, cold, clammy skin
• Rapid, weak pulse
• Increased, shallow breathing rate, stares blankly
What to do:
• Maintain an open airway for the victim
• Call for assistance
• Keep the victim lying down with the head lower than the rest of the body or in
the supine position
• Attempt to control bleeding or cause of shock (if known)
• Keep the victim warm until help arrives
This document is property of Career Employment Consultants, LLC. It cannot be reproduced, transmitted, or copied for any reason without the
written consent from Career Employment Consultants, LLC