Page 9 - PHLEBOTOMY STUDY GUIDE
P. 9
Page 9 of 36
Do not draw blood without orders, always label the tube after you obtain the
specimen.
A. The needle holder is also known as the HUB, the flange on the hub is important
to use during a phlebotomy procedure, it ensures control of the needle. Hubs
may vary depending on the facility.
B. Lab requisition slip, preprinted labels, fine-tooth marker to label tubes.
C. Antiseptic:
• Prepackaged 70% isopropyl alcohol pads are the most commonly
used.
• Chlorhexidine gluconate (Chlora-Prep) used for blood cultures and
arterial punctures, and patients allergic povidone-iodine.
• Povidone-iodine solution is rarely used due to allergic reaction, but
should still with your supplies.
D. Winged infusion sets (Butterfly)
• Used for venipuncture on small veins such as those in the hand. They
are also used for venipuncture in the elderly and pediatric patients.
• Various gauge size
E. Sterile syringes and needles
10-20 ml syringe is used when veins are weak and may collapse. Transfer
safety devices are required when using the syringe method.
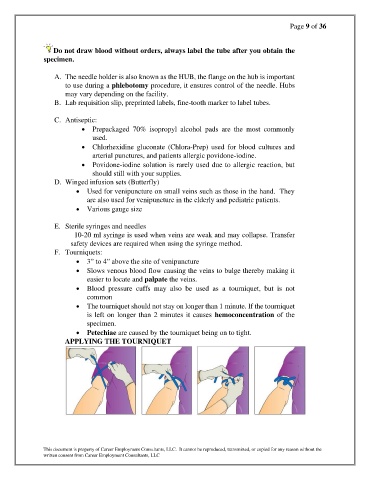
F. Tourniquets:
• 3” to 4” above the site of venipuncture
• Slows venous blood flow causing the veins to bulge thereby making it
easier to locate and palpate the veins.
• Blood pressure cuffs may also be used as a tourniquet, but is not
common
• The tourniquet should not stay on longer than 1 minute. If the tourniquet
is left on longer than 2 minutes it causes hemoconcentration of the
specimen.
• Petechiae are caused by the tourniquet being on to tight.
APPLYING THE TOURNIQUET
This document is property of Career Employment Consultants, LLC. It cannot be reproduced, transmitted, or copied for any reason without the
written consent from Career Employment Consultants, LLC