Page 11 - nutrition
P. 11
Maturitas 143 (2021) 1–9
H. Shakoor et al.
Table 1 Table 1 (continued)
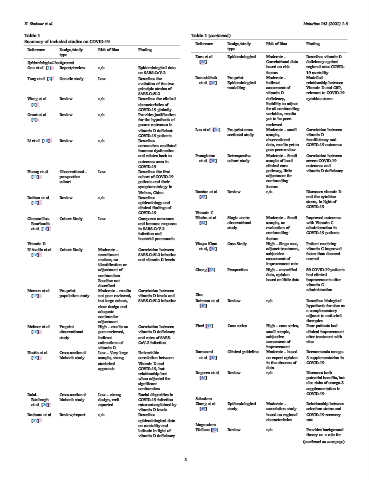
Summary of included studies on COVID-19.
Reference Design/study Risk of Bias Finding
Reference Design/study Risk of Bias Finding type
type
Kara et al. Epidemiological Moderate – Describes vitamin D
Epidemiological background [22] Correlational data deficiency against
Guo et al. [1] Report/review n/a Epidemiological data based on risk regional rates COVID-
on SARS-CoV-2 factors 19 mortality
Tang et al. [2] Genetic study Low Describes the Daneshkhah Pre-print Moderate – Modelled
evolution of the two et al. [23] Epidemiological indirect relationship between
principle strains of modelling assessment of Vitamin D and CRP,
SARS-CoV-2 vitamin D relevant to COVID-19
Wang et al. Review n/a Describes the clinical deficiency, cytokine storm
[3] characteristics of Inability to adjust
COVID-19 globally for all confounding
Grant et al. Review n/a Provides justification variables, results
[9] for the hypothesis of yet to be peer-
poorer outcomes in reviewed
vitamin D deficient Lau et al. [24] Pre-print cross Moderate – small Correlation between
COVID-19 patients sectional study sample, vitamin D
Li et al. [10] Review n/a Describes observational insufficiency and
coronavirus mediated data, results yet to COVID-19 outcomes
immune dysfunction pass peer-review
and relates back to Panagiotou Retrospective Moderate – Small Correlation between
outcomes seen in et al. [25] cohort study sample of local severe COVID-19
COVID-19 clinical care outcomes and
Huang et al. Observational – Low Describes the first pathway, little vitamin D deficiency
[11] prospective cohort of COVID-19 adjustment for
cohort patients and their confounding
symptomatology in factors
Wuhan, China Razdan et al. Review n/a Discusses vitamin D
Rothan et al. Review n/a Describes [27] and the cytokine
[12] epidemiology and storm, in light of
clinical findings of COVID-19
COVID-19 Vitamin C
Giamarellos- Cohort Study Low Compares outcomes Hiedra et al. Single centre Moderate – Small Improved outcomes
Bourboulis and immune response [33] observational sample, no with Vitamin C
et al. [13] in SARS-CoV-2 study evaluation of administration in
infection and confounding COVID-19 patients
bacterial pneumonia factors
Vitamin D Waqas Khan Case Study High – Singe case, Patient receiving
D’Avolio et al. Cohort Study Moderate – Correlation between et al, [34] adjunct treatment, vitamin C improved
[16] recruitment SARS-CoV-2 infection subjective faster than deemed
unclear, no and vitamin D levels. assessment of normal
identification or improvement rate
adjustment of Cheng [35] Perspective High – unverified 50 COVID-19 patients
confounders. data, opinion had clinical
Baseline not based on little data improvements after
described vitamin C
Merzon et al Pre-print Moderate – results Correlation between administration
[17] population study not peer reviewed, vitamin D levels and Zinc
but large cohort, SARS-CoV-2 infection Rahman et al. Review n/a Describes biological
clear design and [40] hypothesis for zinc as
adequate a complementary
confounder adjunct to anti-viral
adjustment therapies
Meltzer et al. Preprint High – results no Correlation between Finzi [41] Case series High – case series, Four patients had
[18] observational peer-reviewed, vitamin D deficiency small sample, clinical improvement
study indirect and rates of SARS- subjective after treatment with
estimations of CoV-2 infection. assessment of zinc
vitamin D. improvement
Hastie et al. Cross-sectional Low – Very large Univariable Barazzoni Clinical guideline Moderate – based Recommends omega-
[19] biobank study sample, strong correlation between et al. [43] on expert opinion 3 supplementation in
statistical Vitamin D and in the absence of COVID-19
approach COVID-19, but data
relationship lost Rogereo et al. Review n/a Discusses both
when adjusted for [44] potential benefits, but
significant also risks of omega-3
confounders supplementation in
Raisi- Cross-sectional Low – strong Racial disparities in COVID-19
Estabragh biobank study design, well COVID-19 infection Selenium
et al. [20] reported rates not explained by Zhang et al. Epidemiological Moderate – Relationship between
vitamin D levels [45] study association study selenium status and
Braiman et al. Review/report n/a Describes based on regional COVID-19 recovery
[21] epidemiological data characteristics rate
on mortality and Magnesium
latitude in light of Wallace [50] Review n/a Provides background
vitamin D deficiency theory on a role for
(continued on next page)
3