Page 11 - MSC & Exosomes in autoimmune
P. 11
3564 Chung et al.
the immunological rejection should be another considera-
tion of the study. The number of WBC was increased at
12 hr after the infarction in both groups as a result of the
pathological process from the brain infarction. There was
no significant increase in the HUCBC group in number
of WBCs after the transplantation of HUBC-derived
MSCs. Number of WBCs remained in the normal range
after the injection of HUCB-derived MSCs (Fig. 7).
Immunohistochemical studies were performed to
detect intraarterially injected HUCB-derived MSCs in
vivo. CM-DiI-labeled HUCB-derived MSCs were
detected around the ischemic lesions in the penumbra
region. In the infarction lesion area, many inflammatory
cells were observed that had autofluorescence. To con-
firm that the observed CM-diI prelabeled cells originated
from the HUCB-derived MSCs, human nuclei antibody
(MAB1281) was used with Alexa Fluor 350 dye, which
had blue fluorescence. Inflammatory cells did not auto-
fluoresce when observed with blue fluorescent micros-
copy. Blue fluorescent cells expressing human nuclei
markers were also observed around the infarction lesion
area. Transplanted HUCB-derived MSCs survived and
migrated toward the infarcted left hemisphere and were
identified at week 4 after transplantation. Migrated
HUCB-derived MSCs had polymorphologic features.
Injected hUBC-derived MSCs did not differentiate into
morphologically complete neural cells, but cells that
were positive for human cell nuclei were observed
around the lesion in the penumbra area by immunohis-
tochemistry. Colocalization of CM-DiI-prelabeled
HUCB-derived MSCs with GFAP- and NeuN-positive
cells suggests that injected HUCB-derived MSCs sur-
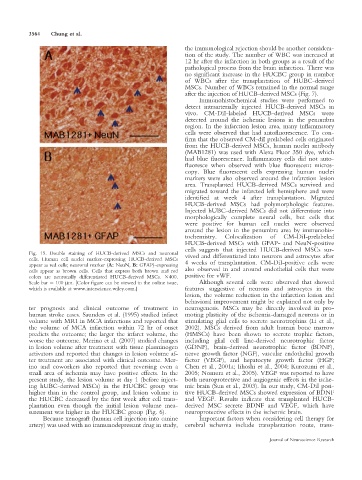
Fig. 15. Double staining of HUCB-derived MSCs and neuronal vived and differentiated into neurons and astrocytes after
cells. Human cell nuclei marker-expressing HUCB-derived MSCs
appear as red cells; neuronal marker (A: NeuN, B: GFAP)-expressing 4 weeks of transplantation. CM-DiI-positive cells were
cells appear as brown cells. Cells that express both brown and red also observed in and around endothelial cells that were
colors are neuronally differentiated HUCB-derived MSCs. 3400. positive for vWF.
Scale bar 5 100 lm. [Color figure can be viewed in the online issue, Although several cells were observed that showed
which is available at www.interscience.wiley.com.] features suggestive of neurons and astrocytes in the
lesion, the volume reduction in the infarction lesion and
behavioral improvement might be explained not only by
ter prognosis and clinical outcome of treatment in neurogenesis. MSCs may be directly involved in pro-
human stroke cases. Saunders et al. (1995) studied infarct moting plasticity of the ischemia-damaged neurons or in
volume with MRI in MCA infarctions and reported that stimulating glial cells to secrete neurotrophins (Li et al.,
the volume of MCA infarction within 72 hr of onset 2002). MSCs derived from adult human bone marrow
predicts the outcome; the larger the infarct volume, the (HMSCs) have been shown to secrete trophic factors,
worse the outcome. Merino et al. (2007) studied changes including glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor
in lesion volume after treatment with tissue plasminogen (GDNF), brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF),
activators and reported that changes in lesion volume af- nerve growth factor (NGF), vascular endothelial growth
ter treatment are associated with clinical outcome. Mer- factor (VEGF), and hepatocyte growth factor (HGF;
ino and coworkers also reported that reversing even a Chen et al., 2001a; Iihoshi et al., 2004; Kurozumi et al.,
small area of ischemia may have positive effects. In the 2005; Nomura et al., 2005). VEGF was reported to have
present study, the lesion volume at day 1 (before inject- both neuroprotective and angiogenic effects in the ische-
ing hUBC-derived MSCs) in the HUCBC group was mic brain (Sun et al., 2003). In our study, CM-DiI posi-
higher than in the control group, and lesion volume in tive HUCB-derived MSCs showed expression of BDNF
the HUCBC decreased by the first week after cell trans- and VEGF. Results indicate that transplanted HUCB-
plantation even though the initial lesion volume mea- derived MSC secrete BDNF and VEGF, which have
surement was higher in the HUCBC group (Fig. 6). neuroprotective effects in the ischemic brain.
Because xenograft (human cell injection into canine Important factors when considering cell therapy for
artery) was used with no immunodepressant drug in study, cerebral ischemia include transplantation route, trans-
Journal of Neuroscience Research