Page 10 - MSC & Exosomes in autoimmune
P. 10
HUCB-Derived MSCs in Canine Cerebral Ischemia 3563
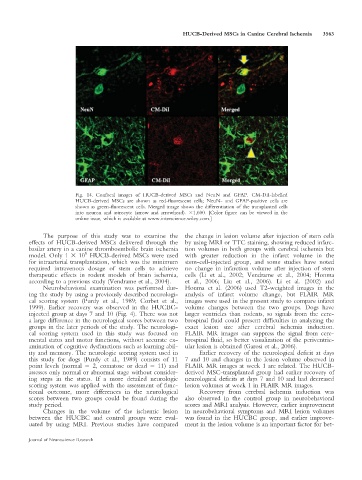
Fig. 14. Confocal images of HUCB-derived MSCs and NeuN and GFAP. CM-DiI-labelled
HUCB-derived MSCs are shown as red-fluorescent cells; NeuN- and GFAP-positive cells are
shown as green-fluorescent cells. Merged image shows the differentiation of the transplanted cells
into neuron and astrocyte (arrow and arrowhead). 31,600. [Color figure can be viewed in the
online issue, which is available at www.interscience.wiley.com.]
The purpose of this study was to examine the the change in lesion volume after injection of stem cells
effects of HUCB-derived MSCs delivered through the by using MRI or TTC staining, showing reduced infarc-
basilar artery in a canine thromboembolic brain ischemia tion volumes in both groups with cerebral ischemia but
6
model. Only 1 3 10 HUCB-derived MSCs were used with greater reduction in the infarct volume in the
for intraarterial transplantation, which was the minimum stem-cell-injected group, and some studies have noted
required intravenous dosage of stem cells to achieve no change in infarction volume after injection of stem
therapeutic effects in rodent models of brain ischemia, cells (Li et al., 2002; Vendrame et al., 2004; Honma
according to a previous study (Vendrame et al., 2004). et al., 2006; Liu et al., 2006). Li et al. (2002) and
Neurobehavioral examination was performed dur- Honma et al. (2006) used T2-weighted images in the
ing the study by using a previously described neurologi- analysis of infarct volume change, but FLAIR MR
cal scoring system (Purdy et al., 1989; Corbet et al., images were used in the present study to compare infarct
1999). Earlier recovery was observed in the HUCBC- volume changes between the two groups. Dogs have
injected group at days 7 and 10 (Fig. 4). There was not larger ventricles than rodents, so signals from the cere-
a large difference in the neurological scores between two brospinal fluid could present difficulties in analyzing the
groups in the later periods of the study. The neurologi- exact lesion size after cerebral ischemia induction.
cal scoring system used in this study was focused on FLAIR MR images can suppress the signal from cere-
mental status and motor functions, without accurate ex- brospinal fluid, so better visualization of the periventric-
amination of cognitive dysfunctions such as learning abil- ular lesion is obtained (Garosi et al., 2006).
ity and memory. The neurologic scoring system used in Earlier recovery of the neurological deficit at days
this study for dogs (Purdy et al., 1989) consists of 11 7 and 10 and changes in the lesion volume observed in
point levels (normal 5 2, comatose or dead 5 11) and FLAIR MR images at week 1 are related. The HUCB-
assesses only normal or abnormal stage without consider- derived MSC-transplanted group had earlier recovery of
ing steps in the status. If a more detailed neurologic neurological deficits at days 7 and 10 and had decreased
scoring system was applied with the assessment of func- lesion volumes at week 1 in FLAIR MR images.
tional outcome, more differences in the neurological Recovery from cerebral ischemia induction was
scores between two groups could be found during the also observed in the control group in neurobehavioral
study period. scores and MRI analysis. However, earlier improvement
Changes in the volume of the ischemic lesion in neurobehavioral symptoms and MRI lesion volumes
between the HUCBC and control groups were eval- was found in the HUCBC group, and earlier improve-
uated by using MRI. Previous studies have compared ment in the lesion volume is an important factor for bet-
Journal of Neuroscience Research