Page 5 - MSC & Exosomes in autoimmune
P. 5
3558 Chung et al.
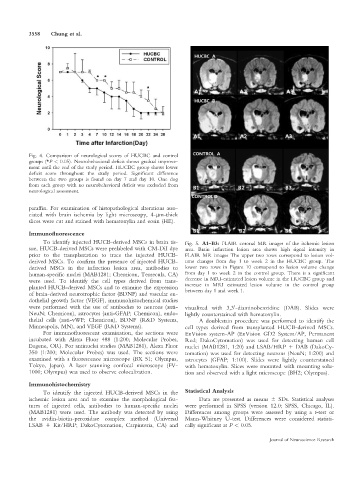
Fig. 4. Comparison of neurological scores of HUCBC and control
groups (*P < 0.05). Neurobehavioral deficit shows gradual improve-
ment until the end of the study period. HUCBC group shows lower
deficit score throughout the study period. Significant difference
between the two groups is found on day 7 and day 10. One dog
from each group with no neurobehavioral deficit was excluded from
neurological assessment.
paraffin. For examination of histopathological alterations asso-
ciated with brain ischemia by light microscopy, 4-lm-thick
slices were cut and stained with hematoxylin and eosin (HE).
Immunofluorescence
To identify injected HUCB-derived MSCs in brain tis- Fig. 5. A1–B3: FLAIR coronal MR images of the ischemic lesion
sue, HUCB-derived MSCs were prelabeled with CM-DiI dye area. Brain infarction lesion area shows high signal intensity in
prior to the transplantation to trace the injected HUCB- FLAIR MR images The upper two rows correspond to lesion vol-
derived MSCs. To confirm the presence of injected HUCB- ume changes from day 1 to week 2 in the HUCBC group. The
derived MSCs in the infarction lesion area, antibodies to lower two rows in Figure 10 correspond to lesion volume change
human-specific nuclei (MAB1281; Chemicon, Temecula, CA) from day 1 to week 2 in the control group. There is a significant
were used. To identify the cell types derived from trans- decrease in MRI-estimated lesion volume in the HUCBC group and
planted HUCB-derived MSCs and to examine the expression increase in MRI estimated lesion volume in the control group
between day 1 and week 1.
of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and vascular en-
dothelial growth factor (VEGF), immunohistochemical studies
0
were performed with the use of antibodies to neurons (anti- visualized with 3,3 -diaminobenzidine (DAB). Slides were
NeuN; Chemicon), astrocytes (anti-GFAP; Chemicon), endo- lightly counterstained with hematoxylin.
thelial cells (anti-vWF; Chemicon), BDNF (R&D Systems, A doublestain procedure was performed to identify the
Minneapolis, MN), and VEGF (R&D Systems). cell types derived from transplanted HUCB-derived MSCs.
For immunofluorescent examination, the sections were EnVision system-AP (EnVision GD2 System/AP, Permanent
incubated with Alexa Fluor 488 (1:200; Molecular Probes, Red; DakoCytomation) was used for detecting human cell
Eugene, OR). For antinuclei studies (MAB1281), Alexa Fluor nuclei (MAB1281, 1:20) and LSAB/HRP 1 DAB (DakoCy-
350 (1:200; Molecular Probes) was used. The sections were tomation) was used for detecting neurons (NeuN; 1:200) and
examined with a fluorescence microscope (BX 51; Olympus, astrocytes (GFAP; 1:100). Slides were lightly counterstained
Tokyo, Japan). A laser scanning confocal microscope (FV- with hematoxylin. Slices were mounted with mounting solu-
1000; Olympus) was used to observe colocalization. tion and observed with a light microscope (BH2; Olympus).
Immunohistochemistry
To identify the injected HUCB-derived MSCs in the Statistical Analysis
ischemic lesion area and to examine the morphological fea- Data are presented as means 6 SDs. Statistical analyses
tures of injected cells, antibodies to human-specific nuclei were performed in SPSS (version 12.0; SPSS, Chicago, IL).
(MAB1281) were used. The antibody was detected by using Differences among groups were assessed by using a t-test or
the avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex method (Universal Mann-Whitney U-test. Differences were considered statisti-
LSAB 1 Kit/HRP; DakoCytomation, Carpinteria, CA) and cally significant at P < 0.05.
Journal of Neuroscience Research