Page 83 - Mesenchymal Stem cells, Exosomes and vitamins in the fight aginst COVID
P. 83
Pain Physician: August 2020 COVID-19 Special Issue 23:S391-S420
quality of life indicators. Conversely,
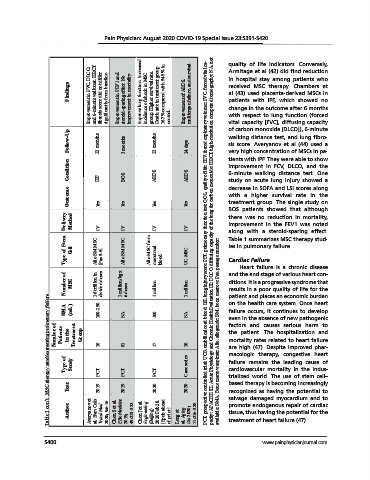
Improvement in FVC, DLCO, and 6-minute walk test. HRCT fibrosis score did not differ significantly from baseline. Improvement in FEV1 and steroid-sparing effect. No improvement in mortality. incidence of shock in MSC group. Higher survival rate. Death rate in treatment group 16.7% compared with 54.5% in Improvement of ARDS, multiorgan failure, and survival. patients with IPF, which showed no
in hospital stay among patients who
Findings Improve lung function. Increased Armitage et al (42) did find reduction
received MSC therapy. Chambers et
al (43) used placenta-derived MSCs in
change in the outcome after 6 months
control.
with respect to lung function (forced
vital capacity [FVC], diffusing capacity
of carbon monoxide [DLCO]), 6-minute
Follow-Up 12 months 3 months 12 months 14 days walking distance test, and lung fibro-
sis score. Averyanov et al (44) used a
very high concentration of MSCs in pa-
tients with IPF. They were able to show
Condition IPF BOS ARDS ARDS improvement in FCV, DLCO, and the
6-minute walking distance test. One
study on acute lung injury showed a
Outcome Yes Yes Yes Yes decrease in SOFA and LSI scores along
with a higher survival rate in the
treatment group. The single study on
Delivery Method IV IV IV IV BOS patients showed that although
there was no reduction in mortality,
improvement in the FEV1 was noted
along with a steroid-sparing effect.
Type of Stem Cell Allo BM MSC [Pas 3-5] Allo BM MSC Allo MSC from menstrual UC MSC PCT, prospective controlled trial; UCB, umbilical cord blood; LSI, lung injury score; PFT, pulmonary function test; QOL, quality of life; FEV, forced expiratory volume;; FVC, forced vital ca- pacity; APACHE III, Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation III; DLCO, diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide; HRCT, high-resolution computed tomography; NA, not
ies in pulmonary failure.
blood
Cardiac Failure
Heart failure is a chronic disease
Number of MSC 1.6 trillion in divided doses 1 million/kg x 6 doses 1 million 1 million ditions. It is a progressive syndrome that
and the end stage of various heart con-
results in a poor quality of life for the
Table 1 con't. MSC therapy studies treating pulmonary failure.
patient and places an economic burden
BMA (mL) 100-150 NA 100 NA on the health care system. Once heart
failure occurs, it continues to develop
even in the absence of new pathogenic
Number of Patients in the Treatment Group 10 81 17 10 available; BMA, Bone marrow aspirate; Allo, allogeneic; BM, bone marrow; Pas, passage number; .. factors and causes serious harm to
the patient. The hospitalization and
mortality rates related to heart failure
are high (47). Despite improved phar-
Type of Study PCT PCT PCT Case series macologic therapy, congestive heart
failure remains the leading cause of
cardiovascular mortality in the indus-
based therapy is becoming increasingly
Year 2019 2019 2020 2020 trialized world. The use of stem cell–
recognized as having the potential to
salvage damaged myocardium and to
Author Averyanov et al, Stem Cells Transl Med 2020; 9:6-16 Chen S et al, EBioMedicine 2019; 49:213-222 Chen J et al, Engineering (Beijing) 2020 Feb 28. [Epub ahead of print] Leng et al, Aging Dis 2020; 11:216-228 promote endogenous repair of cardiac
tissue, thus having the potential for the
treatment of heart failure (47).
S400 www.painphysicianjournal.com