Page 178 - Accounting Principles (A Business Perspective)
P. 178
4. Completing the accounting cycle
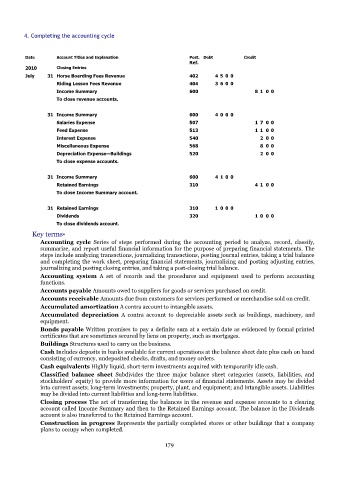
Date Account Titles and Explanation Post. Debt Credit
Ref.
2010 Closing Entries
July 31 Horse Boarding Fees Revenue 402 4 5 0 0
Riding Lesson Fees Revenue 404 3 6 0 0
Income Summary 600 8 1 0 0
To close revenue accounts.
31 Income Summary 600 4 0 0 0
Salaries Expense 507 1 7 0 0
Feed Expense 513 1 1 0 0
Interest Expense 540 2 0 0
Miscellaneous Expense 568 8 0 0
Depreciation Expense—Buildings 520 2 0 0
To close expense accounts.
31 Income Summary 600 4 1 0 0
Retained Earnings 310 4 1 0 0
To close Income Summary account.
31 Retained Earnings 310 1 0 0 0
Dividends 320 1 0 0 0
To close dividends account.
Key terms*
Accounting cycle Series of steps performed during the accounting period to analyze, record, classify,
summarize, and report useful financial information for the purpose of preparing financial statements. The
steps include analyzing transactions, journalizing transactions, posting journal entries, taking a trial balance
and completing the work sheet, preparing financial statements, journalizing and posting adjusting entries,
journalizing and posting closing entries, and taking a post-closing trial balance.
Accounting system A set of records and the procedures and equipment used to perform accounting
functions.
Accounts payable Amounts owed to suppliers for goods or services purchased on credit.
Accounts receivable Amounts due from customers for services performed or merchandise sold on credit.
Accumulated amortization A contra account to intangible assets.
Accumulated depreciation A contra account to depreciable assets such as buildings, machinery, and
equipment.
Bonds payable Written promises to pay a definite sum at a certain date as evidenced by formal printed
certificates that are sometimes secured by liens on property, such as mortgages.
Buildings Structures used to carry on the business.
Cash Includes deposits in banks available for current operations at the balance sheet date plus cash on hand
consisting of currency, undeposited checks, drafts, and money orders.
Cash equivalents Highly liquid, short-term investments acquired with temporarily idle cash.
Classified balance sheet Subdivides the three major balance sheet categories (assets, liabilities, and
stockholders' equity) to provide more information for users of financial statements. Assets may be divided
into current assets; long-term investments; property, plant, and equipment; and intangible assets. Liabilities
may be divided into current liabilities and long-term liabilities.
Closing process The act of transferring the balances in the revenue and expense accounts to a clearing
account called Income Summary and then to the Retained Earnings account. The balance in the Dividends
account is also transferred to the Retained Earnings account.
Construction in progress Represents the partially completed stores or other buildings that a company
plans to occupy when completed.
179