Page 691 - Accounting Principles (A Business Perspective)
P. 691
17. Analysis and interpretation of financial statements
Turnover of operating assets (b/c) 1.11 times 1.09 times
Rate of return on operating assets 14.58% 7.44%
(a/c)
*Calculated as income before income taxes plus net interest expense. This method excludes nonoperating items.
†When companies have no nonoperating assets, total assets are used in the calculation
Net income to net sales (return on sales) ratio Another measure of a company's profitability is the net
income to net sales ratio, calculated as follows:
Net income
Netincome by netsales=
Net sales
This ratio measures the proportion of the sales dollar that remains after deducting all expenses. The
computations for Synotech for 2010 and 2009 are:
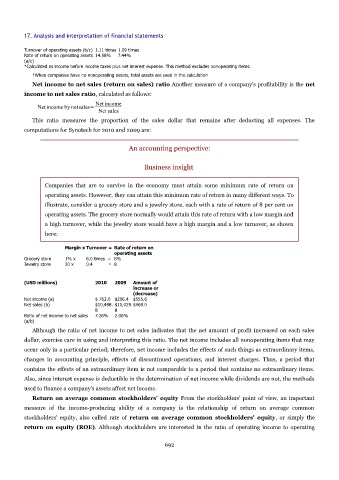
An accounting perspective:
Business insight
Companies that are to survive in the economy must attain some minimum rate of return on
operating assets. However, they can attain this minimum rate of return in many different ways. To
illustrate, consider a grocery store and a jewelry store, each with a rate of return of 8 per cent on
operating assets. The grocery store normally would attain this rate of return with a low margin and
a high turnover, while the jewelry store would have a high margin and a low turnover, as shown
here:
Margin x Turnover = Rate of return on
operating assets
Grocery store 1% x 8.0 times = 8%
Jewelry store 20 x 0.4 = 8
(USD millions) 2010 2009 Amount of
increase or
(decrease)
Net income (a) $ 762.0 $206.4 $555.6
Net sales (b) $10,498. $10,029. $469.0
8 8
Ratio of net income to net sales 7.26% 2.06%
(a/b)
Although the ratio of net income to net sales indicates that the net amount of profit increased on each sales
dollar, exercise care in using and interpreting this ratio. The net income includes all nonoperating items that may
occur only in a particular period; therefore, net income includes the effects of such things as extraordinary items,
changes in accounting principle, effects of discontinued operations, and interest charges. Thus, a period that
contains the effects of an extraordinary item is not comparable to a period that contains no extraordinary items.
Also, since interest expense is deductible in the determination of net income while dividends are not, the methods
used to finance a company's assets affect net income.
Return on average common stockholders' equity From the stockholders' point of view, an important
measure of the income-producing ability of a company is the relationship of return on average common
stockholders' equity, also called rate of return on average common stockholders' equity, or simply the
return on equity (ROE). Although stockholders are interested in the ratio of operating income to operating
692