Page 69 - PowerPoint 演示文稿
P. 69
Lens Aberrations 59
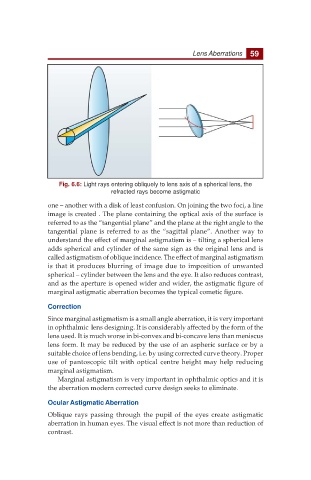
Fig. 6.6: Light rays entering obliquely to lens axis of a spherical lens, the
refracted rays become astigmatic
one – another with a disk of least confusion. On joining the two foci, a line
image is created . The plane containing the optical axis of the surface is
referred to as the “tangential plane” and the plane at the right angle to the
tangential plane is referred to as the “sagittal plane”. Another way to
understand the effect of marginal astigmatism is – tilting a spherical lens
adds spherical and cylinder of the same sign as the original lens and is
called astigmatism of oblique incidence. The effect of marginal astigmatism
is that it produces blurring of image due to imposition of unwanted
spherical – cylinder between the lens and the eye. It also reduces contrast,
and as the aperture is opened wider and wider, the astigmatic figure of
marginal astigmatic aberration becomes the typical cometic figure.
Correction
Since marginal astigmatism is a small angle aberration, it is very important
in ophthalmic lens designing. It is considerably affected by the form of the
lens used. It is much worse in bi-convex and bi-concave lens than meniscus
lens form. It may be reduced by the use of an aspheric surface or by a
suitable choice of lens bending, i.e. by using corrected curve theory. Proper
use of pantoscopic tilt with optical centre height may help reducing
marginal astigmatism.
Marginal astigmatism is very important in ophthalmic optics and it is
the aberration modern corrected curve design seeks to eliminate.
Ocular Astigmatic Aberration
Oblique rays passing through the pupil of the eyes create astigmatic
aberration in human eyes. The visual effect is not more than reduction of
contrast.