Page 71 - PowerPoint 演示文稿
P. 71
Lens Aberrations 61
Coma is associated with the off-axis object points. It occurs because
magnification is the function of the height of the rays of the light. It is the
worst type of aberration as it degrades and deforms the image of a point
object. The funny part is that a lens with considerable coma may produce a
sharp image at the centre of the field, but becomes increasingly blurred
towards the edges.
Correction
The effect of cometic aberration can be minimized by using parabolic curves.
Aspheric lens design helps reduce coma in high plus power.
Ocular Coma
In human eyes, coma gives a comet like image because of small decentration
of the cornea and the lens, which results in different magnification in the
different parts of the pupil. As most of the day time undilated pupil is
around 2-3 mms in size, the ocular cometic aberration does not carry much
of practical importance.
CURVATURE OF FIELD
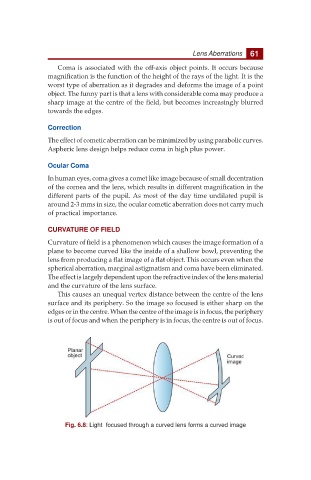
Curvature of field is a phenomenon which causes the image formation of a
plane to become curved like the inside of a shallow bowl, preventing the
lens from producing a flat image of a flat object. This occurs even when the
spherical aberration, marginal astigmatism and coma have been eliminated.
The effect is largely dependent upon the refractive index of the lens material
and the curvature of the lens surface.
This causes an unequal vertex distance between the centre of the lens
surface and its periphery. So the image so focused is either sharp on the
edges or in the centre. When the centre of the image is in focus, the periphery
is out of focus and when the periphery is in focus, the centre is out of focus.
Fig. 6.8: Light focused through a curved lens forms a curved image