Page 107 - PowerPoint Presentation
P. 107
CAVITE STATE UNIVERSITY
T3 CAMPUS
Department of Information Technology DCIT 55 – Advance Database System
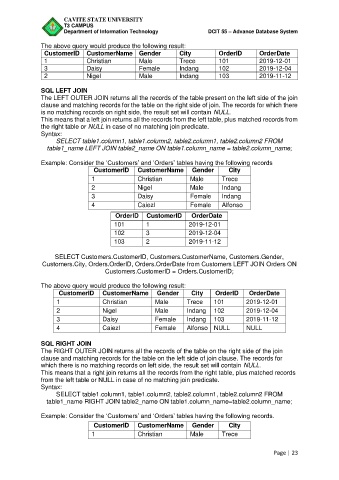
The above query would produce the following result:
CustomerID CustomerName Gender City OrderID OrderDate
1 Christian Male Trece 101 2019-12-01
3 Daisy Female Indang 102 2019-12-04
2 Nigel Male Indang 103 2019-11-12
SQL LEFT JOIN
The LEFT OUTER JOIN returns all the records of the table present on the left side of the join
clause and matching records for the table on the right side of join. The records for which there
is no matching records on right side, the result set will contain NULL.
This means that a left join returns all the records from the left table, plus matched records from
the right table or NULL in case of no matching join predicate.
Syntax:
SELECT table1.column1, table1.column2, table2.column1, table2.column2 FROM
table1_name LEFT JOIN table2_name ON table1.column_name = table2.column_name;
Example: Consider the ‘Customers’ and ‘Orders’ tables having the following records
CustomerID CustomerName Gender City
1 Christian Male Trece
2 Nigel Male Indang
3 Daisy Female Indang
4 Caiezl Female Alfonso
OrderID CustomerID OrderDate
101 1 2019-12-01
102 3 2019-12-04
103 2 2019-11-12
SELECT Customers.CustomerID, Customers.CustomerName, Customers.Gender,
Customers.City, Orders.OrderID, Orders.OrderDate from Customers LEFT JOIN Orders ON
Customers.CustomerID = Orders.CustomerID;
The above query would produce the following result:
CustomerID CustomerName Gender City OrderID OrderDate
1 Christian Male Trece 101 2019-12-01
2 Nigel Male Indang 102 2019-12-04
3 Daisy Female Indang 103 2019-11-12
4 Caiezl Female Alfonso NULL NULL
SQL RIGHT JOIN
The RIGHT OUTER JOIN returns all the records of the table on the right side of the join
clause and matching records for the table on the left side of join clause. The records for
which there is no matching records on left side, the result set will contain NULL.
This means that a right join returns all the records from the right table, plus matched records
from the left table or NULL in case of no matching join predicate.
Syntax:
SELECT table1.column1, table1.column2, table2.column1, table2.column2 FROM
table1_name RIGHT JOIN table2_name ON table1.column_name=table2.column_name;
Example: Consider the ‘Customers’ and ‘Orders’ tables having the following records.
CustomerID CustomerName Gender City
1 Christian Male Trece
Page | 23