Page 108 - PowerPoint Presentation
P. 108
CAVITE STATE UNIVERSITY
T3 CAMPUS
Department of Information Technology DCIT 55 – Advance Database System
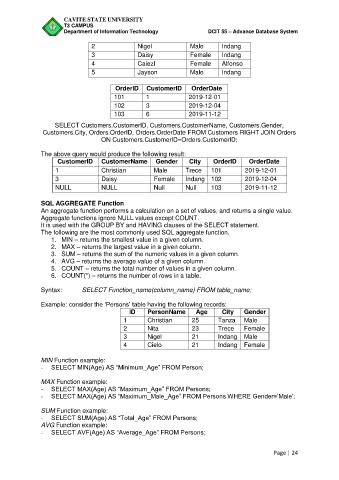
2 Nigel Male Indang
3 Daisy Female Indang
4 Caiezl Female Alfonso
5 Jayson Male Indang
OrderID CustomerID OrderDate
101 1 2019-12-01
102 3 2019-12-04
103 6 2019-11-12
SELECT Customers.CustomerID, Customers.CustomerName, Customers.Gender,
Customers.City, Orders.OrderID, Orders.OrderDate FROM Customers RIGHT JOIN Orders
ON Customers.CustomerID=Orders.CustomerID;
The above query would produce the following result:
CustomerID CustomerName Gender City OrderID OrderDate
1 Christian Male Trece 101 2019-12-01
3 Daisy Female Indang 102 2019-12-04
NULL NULL Null Null 103 2019-11-12
SQL AGGREGATE Function
An aggregate function performs a calculation on a set of values, and returns a single value.
Aggregate functions ignore NULL values except COUNT.
It is used with the GROUP BY and HAVING clauses of the SELECT statement.
The following are the most commonly used SQL aggregate function.
1. MIN – returns the smallest value in a given column.
2. MAX – returns the largest value in a given column.
3. SUM – returns the sum of the numeric values in a given column.
4. AVG – returns the average value of a given column.
5. COUNT – returns the total number of values in a given column.
6. COUNT(*) – returns the number of rows in a table.
Syntax: SELECT Function_name(column_name) FROM table_name;
Example: consider the ‘Persons’ table having the following records:
ID PersonName Age City Gender
1 Christian 25 Tanza Male
2 Nita 23 Trece Female
3 Nigel 21 Indang Male
4 Cielo 21 Indang Female
MIN Function example:
- SELECT MIN(Age) AS “Minimum_Age” FROM Person;
MAX Function example:
- SELECT MAX(Age) AS “Maximum_Age” FROM Persons;
- SELECT MAX(Age) AS “Maximum_Male_Age” FROM Persons WHERE Gender=’Male’;
SUM Function example:
- SELECT SUM(Age) AS “Total_Age” FROM Persons;
AVG Function example:
- SELECT AVF(Age) AS “Average_Age” FROM Persons;
Page | 24