Page 96 - PowerPoint Presentation
P. 96
CAVITE STATE UNIVERSITY
T3 CAMPUS
Department of Information Technology DCIT 55 – Advance Database System
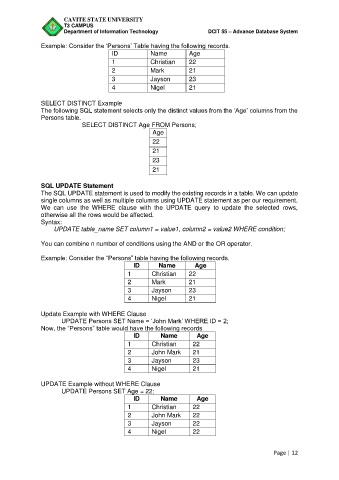
Example: Consider the ‘Persons’ Table having the following records.
ID Name Age
1 Christian 22
2 Mark 21
3 Jayson 23
4 Nigel 21
SELECT DISTINCT Example
The following SQL statement selects only the distinct values from the ‘Age’ columns from the
Persons table.
SELECT DISTINCT Age FROM Persons;
Age
22
21
23
21
SQL UPDATE Statement
The SQL UPDATE statement is used to modify the existing records in a table. We can update
single columns as well as multiple columns using UPDATE statement as per our requirement.
We can use the WHERE clause with the UPDATE query to update the selected rows,
otherwise all the rows would be affected.
Syntax:
UPDATE table_name SET column1 = value1, column2 = value2 WHERE condition;
You can combine n number of conditions using the AND or the OR operator.
Example: Consider the “Persons” table having the following records.
ID Name Age
1 Christian 22
2 Mark 21
3 Jayson 23
4 Nigel 21
Update Example with WHERE Clause
UPDATE Persons SET Name = ‘John Mark’ WHERE ID = 2;
Now, the “Persons” table would have the following records
ID Name Age
1 Christian 22
2 John Mark 21
3 Jayson 23
4 Nigel 21
UPDATE Example without WHERE Clause
UPDATE Persons SET Age = 22;
ID Name Age
1 Christian 22
2 John Mark 22
3 Jayson 22
4 Nigel 22
Page | 12