Page 50 - PC 101 practical notes 24-25..
P. 50
MANSOURA NATIONAL UNIVERSIY
PHARM D- CLINICAL PHARMACY LEVEL I PHARM. ANAL. CHEM. I (PC 101)
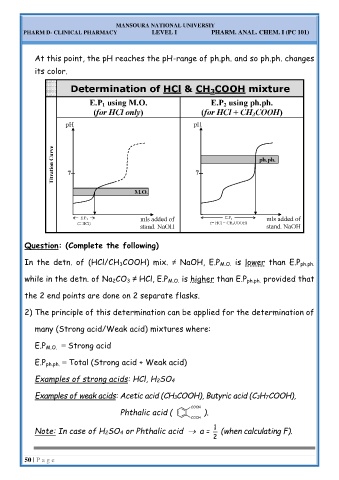
At this point, the pH reaches the pH-range of ph.ph. and so ph.ph. changes
its color.
Question: (Complete the following)
In the detn. of (HCl/CH 3COOH) mix. ≠ NaOH, E.P M.O. is lower than E.P ph.ph.
while in the detn. of Na 2CO 3 ≠ HCl, E.P M.O. is higher than E.P ph.ph. provided that
the 2 end points are done on 2 separate flasks.
2) The principle of this determination can be applied for the determination of
many (Strong acid/Weak acid) mixtures where:
E.P M.O. ≡ Strong acid
E.P ph.ph. ≡ Total (Strong acid + Weak acid)
Examples of strong acids: HCl, H2SO4
Examples of weak acids: Acetic acid (CH3COOH), Butyric acid (C3H7 COOH),
Phthalic acid ( ).
1
Note: In case of H2SO4 or Phthalic acid → a = (when calculating F).
2
50 | P a g e