Page 11 - Group 4_Project_CESP2021
P. 11
Based on the explanation above, it can be concluded that a covalent bond is a
bond that occurs due to the sharing of an electron pair by two atoms. A covalent bond
is formed between two atoms that both want to gain electrons. Generally covalent bonds
are formed by non-metallic elements which can be of the same type (e.g. H2, N2, O2,
Cl2, F2, Br2, I2) and different types (e.g. H2O, CO2, etc.). Compounds that contain only
covalent bonds are called covalent compounds. The use of electron pairs in covalent
bonds can be described by Lewis structures.
A. Lewis Structure
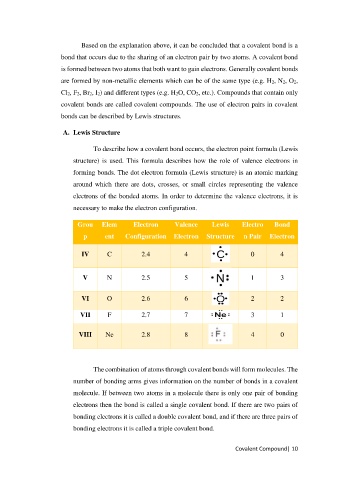
To describe how a covalent bond occurs, the electron point formula (Lewis
structure) is used. This formula describes how the role of valence electrons in
forming bonds. The dot electron formula (Lewis structure) is an atomic marking
around which there are dots, crosses, or small circles representing the valence
electrons of the bonded atoms. In order to determine the valence electrons, it is
necessary to make the electron configuration.
Grou Elem Electron Valence Lewis Electro Bond
p ent Configuration Electron Structure n Pair Electron
IV C 2.4 4 0 4
V N 2.5 5 1 3
VI O 2.6 6 2 2
VII F 2.7 7 3 1
VIII Ne 2.8 8 4 0
The combination of atoms through covalent bonds will form molecules. The
number of bonding arms gives information on the number of bonds in a covalent
molecule. If between two atoms in a molecule there is only one pair of bonding
electrons then the bond is called a single covalent bond. If there are two pairs of
bonding electrons it is called a double covalent bond, and if there are three pairs of
bonding electrons it is called a triple covalent bond.
Covalent Compound| 10