Page 130 - Mathematics Coursebook
P. 130
13.1 Plotting coordinates
13.1 Plotting coordinates
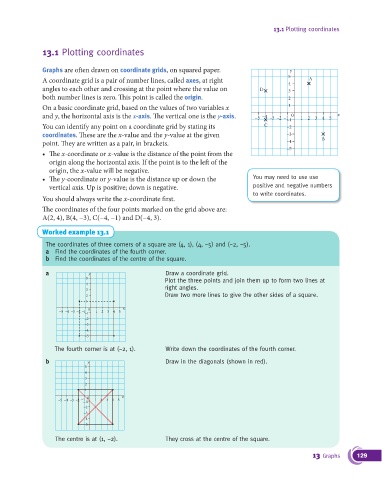
Graphs are o!en drawn on coordinate grids, on squared paper. y
A coordinate grid is a pair of number lines, called axes, at right 5 4 A
angles to each other and crossing at the point where the value on D 3
both number lines is zero. "is point is called the origin. 2
On a basic coordinate grid, based on the values of two variables x 1
and y, the horizontal axis is the x-axis. " e vertical one is the y-axis. –5 –4 –3 –2 –1 –1 0 1 2 3 4 5 x
You can identify any point on a coordinate grid by stating its C –2
coordinates. "ese are the x-value and the y-value at the given –3
point. "ey are written as a pair, in brackets. –4 B
–5
t "e x-coordinate or x-value is the distance of the point from the
origin along the horizontal axis. If the point is to the le! of the
origin, the x-value will be negative.
t "e y-coordinate or y-value is the distance up or down the You may need to use use
vertical axis. Up is positive; down is negative. positive and negative numbers
to write coordinates.
You should always write the x-coordinate #rst.
"e coordinates of the four points marked on the grid above are:
A(2, 4), B(4, −3), C(−4, −1) and D(−4, 3).
Worked example 13.1
The coordinates of three corners of a square are (4, 1), (4, −5) and (−2, −5).
a Find the coordinates of the fourth corner.
b Find the coordinates of the centre of the square.
a y Draw a coordinate grid.
5 Plot the three points and join them up to form two lines at
4
3 right angles.
2 Draw two more lines to give the other sides of a square.
1
0 x
–5 –4 –3 –2 –1 1 2 3 4 5
–1
–2
–3
–4
–5
The fourth corner is at (−2, 1). Write down the coordinates of the fourth corner.
b y Draw in the diagonals (shown in red).
5
4
3
2
1
0 x
–5 –4 –3 –2 –1 1 2 3 4 5
– 1
–2
–3
–4
–5
The centre is at (1, −2). They cross at the centre of the square.
13 Graphs 129