Page 151 - Mathematics Coursebook
P. 151
15.3 Real-life graphs
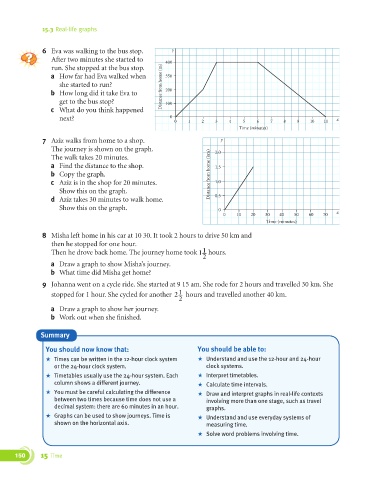
6 Eva was walking to the bus stop. y
After two minutes she started to 400
run. She stopped at the bus stop.
a How far had Eva walked when 350
she started to run? Distance from home (m)
b How long did it take Eva to 200
get to the bus stop? 100
c What do you think happened
next? 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 x
Time (minutes)
7 Aziz walks from home to a shop. y
The journey is shown on the graph. 2.0
The walk takes 20 minutes.
a Find the distance to the shop. 1.5
b Copy the graph. Distance from home (km)
c Aziz is in the shop for 20 minutes. 1.0
Show this on the graph.
d Aziz takes 30 minutes to walk home. 0.5
Show this on the graph. 0
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 x
Time (minutes)
8 Misha left home in his car at 10 30. It took 2 hours to drive 50 km and
then he stopped for one hour.
1
Then he drove back home. The journey home took 1 hours.
2
a Draw a graph to show Misha’s journey.
b What time did Misha get home?
9 Johanna went on a cycle ride. She started at 9 15 am. She rode for 2 hours and travelled 30 km. She
1
stopped for 1 hour. She cycled for another 2 hours and travelled another 40 km.
2
a Draw a graph to show her journey.
b Work out when she finished.
Summary
You should now know that: You should be able to:
+ Times can be written in the 12-hour clock system + Understand and use the 12-hour and 24-hour
or the 24-hour clock system. clock systems.
+ Timetables usually use the 24-hour system. Each + Interpret timetables.
column shows a different journey. + Calculate time intervals.
+ You must be careful calculating the difference + Draw and interpret graphs in real-life contexts
between two times because time does not use a involving more than one stage, such as travel
decimal system: there are 60 minutes in an hour. graphs.
+ Graphs can be used to show journeys. Time is + Understand and use everyday systems of
shown on the horizontal axis. measuring time.
+ Solve word problems involving time.
150 15 Time