Page 63 - Mathematics Coursebook
P. 63
End of unit review
Summary
You should now know that: You should be able to:
+ Lines, angles and shapes can be identified by + Label lines, angles and shapes.
putting letters on the corners. + Estimate, measure and draw angles of any size.
+ Reflex angles are greater than 180°. + Calculate the sum of angles at a point, on a
+ A protractor can be used to measure angles. straight line and in a triangle.
+ The sum of the angles meeting at a point on one + Prove that vertically opposite angles are equal.
side of a straight line is 180°. + Derive and use the property that the angle sum of
+ The sum of the angles in a triangle is 180° and this a quadrilateral is 360°.
fact can be used to calculate angles. + Solve simple angle problems, and explain reasoning.
+ The angles at a point add up to 360° and this fact + Start to recognise the angular connections with
can be used to calculate angles. parallel lines.
+ Vertically opposite angles are equal. + Recognise and use spatial relationships in two
+ There are connections between the angles formed dimensions.
when a transversal crosses parallel lines. + Work logically and draw simple conclusions.
End of unit review
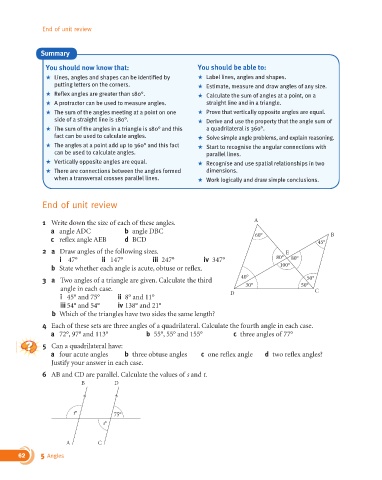
1 Write down the size of each of these angles. A
a angle ADC b angle DBC 60° B
c reflex angle AEB d BCD 45°
2 a Draw angles of the following sizes. E
i 47° ii 147° iii 247° iv 347° 80° 80°
b State whether each angle is acute, obtuse or reflex. 100°
40° 50°
3 a Two angles of a triangle are given. Calculate the third
30° 50°
angle in each case. C
i 45° and 75° ii 8° and 11° D
iii 54° and 54° iv 138° and 21°
b Which of the triangles have two sides the same length?
4 Each of these sets are three angles of a quadrilateral. Calculate the fourth angle in each case.
a 72°, 97° and 113° b 55°, 55° and 155° c three angles of 77°
5 Can a quadrilateral have:
a four acute angles b three obtuse angles c one reflex angle d two reflex angles?
Justify your answer in each case.
6 AB and CD are parallel. Calculate the values of s and t.
B D
t° 75°
s°
A C
62 5 Angles