Page 96 - Mathematics Coursebook
P. 96
8.4 Symmetry properties of triangles, special quadrilaterals and polygons
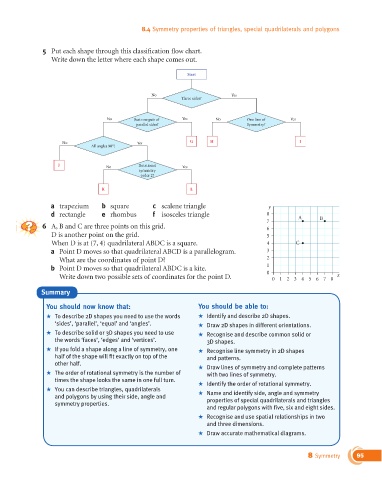
5 Put each shape through this classification flow chart.
Write down the letter where each shape comes out.
Start
No Yes
Three sides?
No Just one pair of Yes No One line of Yes
parallel sides? Symmetry?
No Yes G H I
All angles 90°?
J No Rotational Yes
symmetry
order 2?
K L
a trapezium b square c scalene triangle y
d rectangle e rhombus f isosceles triangle 8 A
7 B
6 A, B and C are three points on this grid. 6
D is another point on the grid. 5
When D is at (7, 4) quadrilateral ABDC is a square. 4 C
a Point D moves so that quadrilateral ABCD is a parallelogram. 3
What are the coordinates of point D? 2
1
b Point D moves so that quadrilateral ABDC is a kite.
Write down two possible sets of coordinates for the point D. 0 0 1 2 345 6 7 8 x
Summary
You should now know that: You should be able to:
+ To describe 2D shapes you need to use the words + Identify and describe 2D shapes.
‘sides’, ‘parallel’, ‘equal’ and ‘angles’. + Draw 2D shapes in different orientations.
+ To describe solid or 3D shapes you need to use + Recognise and describe common solid or
the words ‘faces’, ‘edges’ and ‘vertices’. 3D shapes.
+ If you fold a shape along a line of symmetry, one + Recognise line symmetry in 2D shapes
half of the shape will fit exactly on top of the and patterns.
other half.
+ Draw lines of symmetry and complete patterns
+ The order of rotational symmetry is the number of with two lines of symmetry.
times the shape looks the same in one full turn.
+ Identify the order of rotational symmetry.
+ You can describe triangles, quadrilaterals
and polygons by using their side, angle and + Name and identify side, angle and symmetry
symmetry properties. properties of special quadrilaterals and triangles
and regular polygons with five, six and eight sides.
+ Recognise and use spatial relationships in two
and three dimensions.
+ Draw accurate mathematical diagrams.
8 Symmetry 95