Page 4 - Asam Basa
P. 4
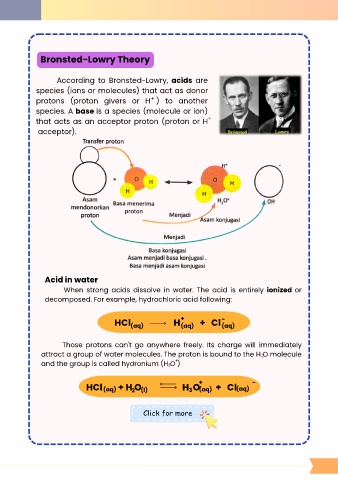
Bronsted-Lowry Theory
According to Bronsted-Lowry, acids are
species (ions or molecules) that act as donor
+
protons (proton givers or H ) to another
species. A base is a species (molecule or ion)
that acts as an acceptor proton (proton or H +
acceptor).
Acid in water
When strong acids dissolve in water. The acid is entirely ionized or
decomposed. For example, hydrochloric acid following:
+
HCl H + Cl -
(aq)
(aq)
(aq)
Those protons can't go anywhere freely. Its charge will immediately
attract a group of water molecules. The proton is bound to the H O molecule
2
+
and the group is called hydronium (H O )
3
+ -
HCl + H O H O + Cl(aq)
(aq)
(aq)
2
(l)
3
Click for more